Introduction: A safe workplace is a sound business.
A safe workplace is not just a legal requirement; it’s a fundamental element of a successful business strategy. When employees feel safe and secure, their productivity increases, morale improves, and turnover rates decrease. In contrast, negligence in safety can lead to accidents, injuries, and even litigation, which can severely impact a company’s reputation and bottom line. Therefore, prioritizing safety in the workplace is a smart investment for any organization. We will unveil the 20 proven and best ways to improve safety performance in the workplace.
Why Is Safety Performance Important?
Achieving good safety performance in the workplace is crucial for several reasons, encompassing employee well-being, organizational efficiency, and compliance with legal standards. Below are some key points highlighting the importance of safety performance:
- Protection of Employees
Safety performance is of primary importance in protecting employees from workplace hazards. A strong safety program reduces the risk of injuries and illnesses. By prioritizing safety, organizations demonstrate their commitment to the health and welfare of their employees. - Reduction of Costs
Injuries and accidents in the workplace can lead to significant costs, including medical expenses, lost productivity, and increased insurance premiums. By reducing incidents and their associated costs (such as medical expenses, legal fees, and insurance premiums), effective safety performance can lead to significant financial savings for the organization. By improving safety performance, businesses can minimize these direct and indirect costs associated with workplace incidents, ultimately enhancing their financial health. - Legal Compliance
Employers must adhere to regulations set forth by occupational safety and health agencies, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States. A strong safety performance record ensures compliance with these necessary legal frameworks, helping organizations avoid potential fines, legal liabilities, and investigations. - Enhanced Productivity
Safe work environments promote higher levels of productivity. When employees feel secure, they can concentrate on their tasks without the distraction of worrying about potential hazards. Additionally, fewer accidents mean reduced downtime due to injuries, allowing Workers who see that their safety is valued smoother operations and heightened productivity. - Boosted Employee Morale and Retention
Prioritizing safety significantly impacts employee morale. Workers who see that their safety is valued are likelier to feel engaged and satisfied with their jobs. This commitment to safety can improve retention rates, as employees are less likely to seek employment elsewhere when they feel protected and valued in their current roles. - Improved Company Reputation
A robust safety record enhances a company’s reputation among clients, customers, and stakeholders. Organizations known for high safety standards are often perceived as more trustworthy, responsibly managed, and committed to quality. This positive reputation can attract new business opportunities, customers, clients, partnerships and potential employees who value safety and responsibility, further contributing to organizational success. - Cultivation of a Safety Culture
Achieving good safety performance leads to developing a strong safety culture within an organization. This culture promotes shared values and behaviours related to safety, encouraging all employees to take an active role in identifying and mitigating risks. A proactive approach to safety promote continuous improvement and innovation regarding safety practices. - Sustainability
A robust safety performance contributes to environmental sustainability by minimizing workplace incidents that can lead to environmental harm. By cultivating a safety culture, organisations can protect their workforce and ensure that their operations do not negatively impact the environment, supporting broader sustainability goals.
In summary, good safety performance is fundamental for protecting employees and cultivating a productive, efficient, and positive workplace environment. As a safety professional, you may face the challenge of managing health and safety with limited resources. In such cases, flexible and adaptable strategies are essential for managing health and safety within resource constraints.
By focusing on safety, organizations can reap the benefits of improved morale, reduced costs, legal compliance, and enhanced reputation, all of which are critical components of long-term success.
How to Improve Safety Performance at the Workplace?
Creating a safe work environment is not just a regulatory obligation; it’s a moral responsibility that organizations owe to their employees. Effective safety performance boosts morale, enhances productivity, saves finances and enables a culture of care.
Ensuring a safe workplace is crucial for both employee well-being and overall productivity. When workers feel secure, they are more inclined to perform at their best. Here’s how to improve safety performance at your workplace.
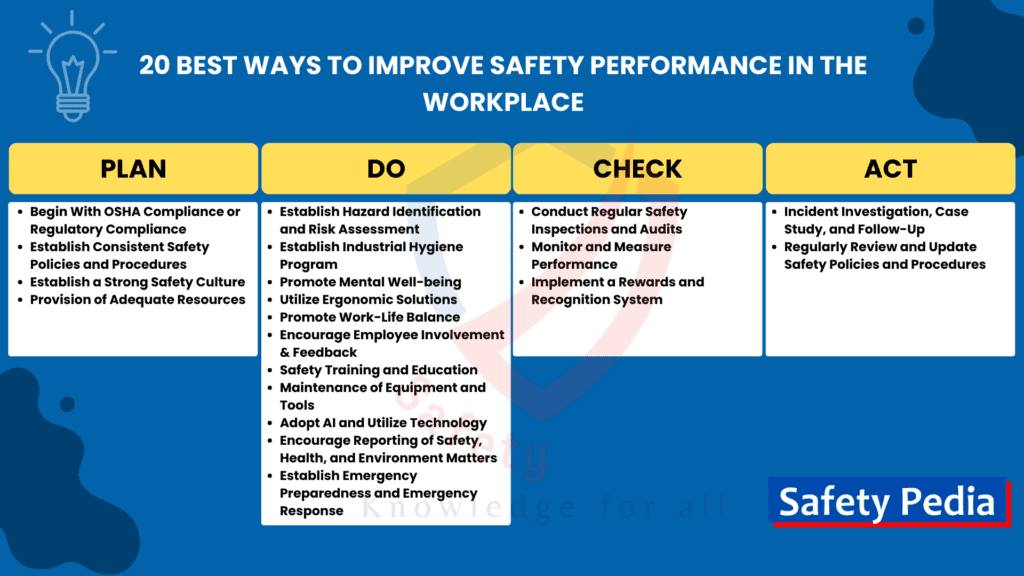
Here are the 20 best ways that can lead to tangible improvements in workplace safety performance:
1. Begin With OSHA Compliance or Regulatory Compliance
To improve safety performance, the first step for any organization should be to ensure compliance with the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines. These comprehensive standards cover all essential aspects such as General Industry Standards, Construction Standards, Maritime Standards, Agriculture Standards, health standards, and various specialized standards (e.g., Hazardous Materials Management, sanitation, first aid, hazardous materials management, ventilation, personal protective equipment, and safety exits).
Adhering to these regulations is a legal obligation and a critical measure to protect workers and reduce the risk of accidents. A thorough review of OSHA requirements is the foundation for any safety improvement initiative, allowing businesses to identify gaps in their safety protocols. It is crucial to recognize that OSHA compliance represents just the beginning of a more expansive safety strategy; organizations should proactively address potential safety hazards, even those not explicitly covered by regulations, to mitigate liability risks.
By OSHA compliance, companies can create a safer work environment, enhance their reputation, and ultimately contribute to improved operational efficiency and profitability.
Upholding Local Safety Regulations for Businesses Outside the US
It is imperative for businesses operating outside of the United States to strictly adhere to their respective country-specific safety, health, and environmental regulations. Compliance with local laws is not merely a legal obligation but a fundamental aspect of operational integrity and corporate responsibility.
Each country has unique safety standards designed to protect its workforce and the environment, and failing to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties, reputational damage, and, most importantly, endanger employees’ lives. Companies must actively engage with local regulatory bodies, ensuring their safety programs are aligned with international best practices and tailored to meet local requirements.
By local regulatory compliance and enabling a culture of safety that respects and integrates local laws, businesses can enhance their operational reliability, build trust with stakeholders, and significantly reduce risks associated with non-compliance.
Adhering to International Labor Organization Standards for Workplace Safety
In an era where workplace safety should be a universal priority, businesses outside the US—especially in countries with lax occupational safety regulations—must take proactive measures by adhering to the International Labour Organization (ILO) occupational safety and health guidelines.
Failing to adopt these comprehensive standards risks workers and exposes companies to significant liabilities and reputational damage. By implementing ILO guidelines, organizations can cultivate a safer work environment that facilitates employee well-being, enhances productivity, and mitigates the likelihood of costly accidents. It’s not merely a suggestion; it’s an imperative for responsible business conduct.
In today’s global economy, companies prioritising health and safety will protect their workforce and gain a competitive edge by attracting talent and ensuring operational sustainability.
To ensure legal compliance, ILO compliance, and local country compliance for improving safety performance, organizations can implement the following actionable items:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Regularly assess current safety policies and practices against local laws, ILO guidelines, and industry standards. Ensure all safety protocols meet or exceed OSHA standards. | Compliance & SHE Team | Quarterly |
| 2 | Identify gaps and areas of non-compliance that need to be addressed. | Risk Assessment Team | Quarterly |
| 3 | Incorporate comprehensive safety policies that reflect both legal requirements and best practices. | Safety Manager | 2 months |
| 4 | Ensure these policies are regularly updated to comply with new regulations or changes in local laws. | Legal/Compliance Officer | Bi-Annual |
| 5 | Automate compliance tracking and reporting to reduce administrative burdens and enhance accuracy. | Software Administrator & EHS Team | 4 months |
| 6 | Maintain open communication with local regulatory bodies to stay informed about changes in safety regulations. | Compliance Officer | Ongoing |
| 7 | Leverage digital tools and software for efficient safety management, including incident reporting, inspection checklists, and policy management. | IT Team | 3 months |
| 8 | Collaborate with local authorities to ensure compliance with community safety standards and initiatives. | Safety Committee | As needed |
By implementing these actionable items, organizations can enhance their safety performance and ensure compliance with legal, ILO, and local regulations, ultimately promoting a safer workplace environment.
2. Establish Consistent Safety Policies and Procedures
To enhance safety performance within the workplace, it is essential to implement robust safety programs and policies that are consistently applied across all levels of the organization. This begins with establishing clear safety standards and procedures that are communicated effectively to all employees. Regular training sessions should be conducted to ensure that everyone understands these protocols and can execute them proficiently.
Additionally, it is vital to align safety policies with the organization’s overall goals and regulatory requirements, encouraging an environment where safety is prioritized as a core value. Consistency in enforcing these policies is crucial; it builds trust among employees and reinforces the importance of safety in daily operations. By regularly reviewing and updating safety programs to reflect changing circumstances, potential hazards, and feedback from staff, organizations can maintain a proactive stance on safety and encourage a culture of continuous improvement.
This systematic approach mitigates risks of accidents and injuries and cultivates a sense of shared responsibility among all employees, ultimately leading to improved safety performance and overall workplace morale.
Here’s a list of actions to develop and maintain consistent safety policies and procedures that can significantly improve safety performance within an organization:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Develop comprehensive safety policies that outline expectations, responsibilities, and procedures for all employees that reflect best practices and regulatory requirements. | Safety Manager | 3 months |
| 2 | Create SOPs for all critical tasks, ensuring they include specific safety measures. | Department Heads | 2 months |
| 3 | Ensure policies are easily accessible and easy to understand | HR/Compliance Team | 2 weeks |
| 4 | Involve employees in developing and reviewing safety policies to encourage a culture of shared responsibility. Engage employees in the review process to gain insights and perspectives. | Safety Committee | Ongoing (every quarter) |
| 5 | Involve employees in developing and reviewing safety policies to create a shared responsibility culture. | Team Leads/Safety Champions | Annually |
| 6 | Offer regular training sessions and workshops to update employees on safety protocols and best practices. | Training Coordinator | Quarterly |
| 7 | Regularly communicate updates on safety policies and performance metrics to all staff. | Communications Team | Monthly |
| 8 | Set a schedule for reviewing and updating safety policies and procedures to reflect regulations, technology, or organizational structure changes. | Safety Compliance Officer | Every 6 months |
By implementing these actions, organizations can create a consistent framework for safety policies and procedures that enhance safety performance and promote a workplace safety culture.
3. Establish a Strong Safety Culture
Creating a strong safety culture is fundamental to enhancing organisational safety performance. This involves encouraging an environment where all employees feel empowered and responsible for their safety and that of their colleagues. To establish such a culture, leadership must prioritize safety at all levels, demonstrating commitment through consistent communication, training, and engagement initiatives. Encouraging open dialogue about safety concerns, recognizing and rewarding safe behaviours, and actively involving employees in safety meetings can significantly enhance awareness and participation.
Moreover, by integrating safety into the organization’s core values, yearly resolutions and daily practices, we reinforce its importance, ensuring that every team member understands their role in promoting a safe workplace. By embedding safety into the organizational ethos, employees are more likely to adopt positive safety behaviours, leading to improved health outcomes and reduced incidents.
Establishing a strong safety culture in the workplace requires a commitment from all levels of the organization, from leadership to employees. Here’s a list of actionable steps that can help create and maintain a positive safety culture:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Ensure that leaders at all levels demonstrate a clear commitment to safety by prioritizing it in decision-making processes. | Senior Management | Ongoing |
| 2 | Cultivate an environment where employees feel comfortable voicing safety concerns without fear of retribution. | HR Director and Safety Committee | Ongoing |
| 3 | Encourage the sharing of safety-related ideas and improvements from all employees. | Team Leads | Monthly |
| 4 | Offer specialized training for managers and supervisors on how to cultivate a safety-oriented workplace. | Training Coordinator | Quarterly |
| 5 | Shift from a blame-centric approach to a forward-looking accountability model that focuses on preventing future incidents. | Safety Manager | Ongoing |
| 6 | Set clear safety performance expectations and hold all employees accountable to those standards. | Supervisors and HR | Annually |
| 7 | Recognize and reward employees who contribute to safety improvements and uphold safety standards. | Recognition Committee | Quarterly |
| 8 | Involve employees in safety committees to ensure their voices are heard in safety planning and decision-making. | Safety Committee Chairperson | Ongoing |
| 9 | Encourage employees to participate in hazard identification and risk assessment processes. | Supervisors | As part of risk assessments (every quarter) |
| 10 | Implement a suggestion system for employees to propose safety enhancements or report hazards. | IT Team and Safety Committee | 2 months |
| 11 | Share results with all employees to promote transparency and collective responsibility. | Communications Team | Quarterly |
| 12 | Share case studies and lessons learned constructively to prevent recurrence and educate the workforce. | Safety Manager | After every incident |
| 13 | Regularly revisit and refine safety strategies to address emerging risks and changes in the workplace. | Safety Committee | Annually |
| 14 | Recognize and celebrate safety milestones and achievements to promote a positive safety culture. | Safety Committee | Quarterly |
| 15 | Promote success stories that highlight safe practices and reinforce the importance of safety in everyday operations. | Safety Committee | Quarterly |
By implementing these actions, organizations can create a robust safety culture that prioritizes the well-being of all employees and contributes to overall operational success.
4. Establish Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment
To enhance safety performance, it is crucial to establish a systematic approach to hazard identification and risk assessment. This process begins with conducting comprehensive hazard assessments to identify and evaluate potential risks within the workplace.
Organizations can systematically uncover workplace hazards and determine their severity and likelihood of occurrence by utilising methodologies such as job safety analysis and process hazard analysis. Involving informal leaders who already have respect among their peers in the safety committee can facilitate greater buy-in and encourage collective responsibility for safety.
Regularly analyzing accident history and performing gap analyses against OSHA requirements can reveal deficiencies and guide the development of appropriate risk management control measures. Furthermore, promoting a culture of continuous improvement ensures that these assessments are not one-time activities but are integrated into daily operations, promoting ongoing vigilance and adaptation.
To ensure effective hazard identification and risk assessment, thereby improving safety performance, the following actions can be implemented:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Form a committee that includes informal leaders and representatives from different levels of the organization to oversee safety initiatives, including hazard assessments and safety program evaluations. | Operation Manager | Quarterly/Annually |
| 2 | Implement systematic evaluations of the workplace to identify safety hazards. Use methodologies such as Job Safety Analysis (JSA) and Process Hazard Analysis (PHA) to ensure all potential risks are identified. | Safety Officer/Operations Team | Semi-Annually/Annually |
| 3 | Develop and document clear procedures based on risk management reviews, ensuring they are accessible to all employees. Ensure that these procedures are regularly updated based on new findings or changes in operational processes. | Safety Officer/Compliance Team | Annually |
| 4 | Review and analyze past incidents and near misses to identify trends and root causes. Use this data to inform training and hazard control measures. | Safety Officer/Incident Review Team | Quarterly/After Each Incident |
| 5 | Develop and conduct safety training for all personnel, emphasizing the importance of hazard recognition and reporting. Include refresher training at regular intervals to maintain awareness. | Training Team/Safety Officer | Ongoing/Annually |
| 6 | Track and analyze safety metrics regularly, such as near misses, safety observations, and hazard identifications. Use this data to spot trends and potential safety issues before incidents occur. | Safety Officer/Operations Team | Annually/As Needed |
| 7 | Encourage open communication regarding safety concerns and empower employees at all levels to report hazards without fear of reprisal. Recognize and reward proactive safety behavior. | Management/HR | Ongoing/Quarterly |
| 8 | Track and analyze safety metrics regularly, such as near misses, safety observations, and hazard identifications. Use this data to spot trends and potential safety issues before incidents occur. | Safety Officer/Data Analyst | Monthly/Quarterly |
| 9 | Involve employees in safety initiatives, such as conducting 6S audits and participating in safety drills. Their involvement can provide valuable insights into potential hazards. | Safety Committee/Team Leads | Quarterly/Annually |
| 10 | Promote adherence to established safety procedures and protocols. Regularly audit compliance and address non-compliance issues immediately. | Compliance Officer/Managers | Ongoing/Semi-Annually |
| 11 | Establish a system for collecting employee feedback on hazard identification processes to improve safety by continuously implementing policies, procedures, and safe practices. | Safety Officer/HR | Ongoing/Quarterly |
| 12 | Ensure that safety is integrated into the overall business strategy, making it a core value rather than a standalone initiative. This alignment can drive greater engagement and commitment from all levels of the organization. | Executive Management | Ongoing/Annually |
Implementing these actions can help create a proactive safety environment that emphasizes hazard identification and risk assessment, ultimately leading to improved safety performance across the organization.
5. Establish Industrial Hygiene Program
Establishing industrial hygiene is a critical component of maintaining a safe and healthy workplace. This involves identifying and controlling environmental factors that may adversely affect employees’ occupational health and well-being.
Start this by conducting thorough assessments to identify potential hazards such as chemical exposure, airborne contaminants, and noise levels. Implementing effective ventilation systems, proper material storage, and regular monitoring of hazardous substances can significantly mitigate risks. Training employees on the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and safe handling practices is also essential. Regular audits and health screenings can help ensure industry standards and regulations compliance.
Prioritizing industrial hygiene, organizations protect their workforce and enhance productivity and morale, ultimately promoting a culture of safety that resonates throughout the entire organization.
To establish industrial hygiene and improve safety performance in the workplace, consider implementing the following actions:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Conduct a workplace hazard assessment to identify potential chemical, physical, biological, and ergonomic risks. | Industrial Hygienist | Week 1-4 |
| 2 | Develop a comprehensive Industrial Hygiene Program, including policies and standard operating procedures (SOPs). | EHS (Environment, Health & Safety) Team | Week 5-8 |
| 3 | Implement regular air, noise, chemical exposure, biological, lighting, and radiation monitoring to assess exposure levels. | Industrial Hygienist | Ongoing, monthly |
| 4 | Create Similar Exposure Groups (SEGs) and monitor exposure levels accordingly. | Industrial Hygienist | Week 4-6 |
| 5 | Regularly review and update assessments to reflect changes in the workplace. | HSE Manager | Annually/After Workplace Changes |
| 6 | Train employees on hazard recognition and safe work practices related to industrial hygiene. | Training Coordinator | Week 9-12 |
| 7 | Provide and maintain appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) for identified hazards. | Procurement & Safety Team | Week 8-10 |
| 8 | Invest in purchasing advanced monitoring equipment for accurate hazard assessment. | Procurement Team | Week 6-8 |
| 9 | Ensure regular calibration and maintenance of monitoring equipment to maintain accuracy. | Equipment Technician | Monthly, ongoing |
| 10 | Conduct chemical inventory and ensure proper labeling and storage per regulatory standards. | Chemical Safety Officer | Week 5-7 |
| 11 | Implement the use of biosafety cabinets for handling hazardous biological materials. | Laboratory Manager | Week 8-10 |
| 12 | Generate checklists wisely to ensure nothing is overlooked while planning the inspection and audit process. | Safety Committee/Industrial Hygiene Team | Each Audit |
| 13 | Perform regular inspections and schedule audits to ensure compliance with IH program standards. | Industrial Hygiene Team & Facilities Team | Monthly |
| 14 | Establish a system for employees to report hygiene-related concerns or near-misses. | Safety Manager | Week 8 |
| 15 | Implement a health surveillance program to monitor employees health exposed to workplace hazards. | Occupational Health Team | Week 8-12, ongoing |
| 16 | Evaluate program effectiveness through periodic audits and update the program as needed. | EHS Team | Every 6 months |
| 17 | Stay informed about changes in health regulations and best practices for industrial hygiene. | Safety Officer/Legal Team | Ongoing/Annually |
By taking these actions, organizations can significantly enhance their industrial hygiene practices, improving safety performance and a healthier work environment.
6. Provision of Adequate Resources
Organisations must ensure adequate resources are allocated to safety initiatives to enhance safety performance. This includes financial investment and the provision of necessary tools, equipment, training, and personnel. Employees with access to the right resources are better equipped to follow safety protocols and respond effectively to potential hazards.
Organizations can encourage an environment where safety is a shared responsibility and integral to daily operations by prioritizing resource allocation for safety, industrial hygiene, occupational health and the environment.
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Allocate resources for safety initiatives, training, and equipment and emergency preparedness | Management Team & Finance Department | Annually (Budget Cycle) |
| 2 | Conduct a comprehensive needs assessment to identify safety resource gaps. | Safety Officer | Annually |
| 4 | Establish and maintain safety committees to oversee resource allocation and needs. | HR/Safety Manager | Ongoing |
| 5 | Procure and provide adequate safety equipment to enhance workplace safety performance and fully comply with all relevant safety regulations. | Procurement Team | Biannually |
| 6 | Procure and provide high-quality personal protective equipment (PPE) for all employees. | Procurement Team | Biannually |
| 7 | Implement and maintain safety management software to streamline communication and reporting. | IT Department | Within 3 Months |
| 8 | Schedule mandatory safety drills and training sessions, ensuring complete employee participation. | Training Coordinator | Every 6 Months |
| 9 | Forge partnerships with external safety organizations or consultants to enhance expert guidance. | Safety Manager | As Needed |
| 10 | Establish an accessible feedback mechanism for employees to propose actionable safety improvements. | HR Department | Within 1 Month |
| 11 | Prioritize investment in the occupational and mental well-being of employees through dedicated programs. | HR and Safety Committee | Ongoing |
| 12 | Secure resources for third-party audits and licensing to ensure compliance with safety standards. | Compliance Officer | Annually |
| 13 | Strategically invest in acquiring international safety certifications such as ISO 45001 and ISO 14001 to elevate workplace safety standards. | Management Team | Within 12 Months |
Organizations can significantly improve their health, safety and environmental performance by taking these actions.
7. Promote Mental Well-being
Promoting mental well-being is an essential component of improving safety performance in the workplace. When employees feel mentally healthy, they are more focused, engaged, and capable of adhering to safety protocols. Implementing programs that support mental health—such as stress management workshops, access to counseling services, and promoting a healthy work-life balance—can significantly reduce workplace stressors that contribute to accidents and errors.
Additionally, encouraging an open environment where employees feel comfortable discussing mental health challenges without fear of stigma encourages a culture of support and trust. By prioritising mental well-being, organizations not only enhance the safety of their work environment but also boost overall morale and productivity, creating a more resilient workforce prepared to tackle challenges effectively.
Furthermore, Emotional intelligence (EI) can play a significant role in improving safety performance within workplaces. Workers with high emotional intelligence are more likely to recognize their emotions, such as stress or fatigue, which can impair judgment and lead to accidents.
Here’s a list of actions that organizations can implement to support their employees’ mental health and, in turn, improve safety outcomes:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Integrate mental health considerations into existing safety policies and procedures, ensuring they are part of overall safety performance evaluations. | SHE Team | Week 10-12 |
| 2 | Organize awareness campaigns that educate employees about mental health issues, available resources, and the importance of seeking help. | SHE & HR Team | Quarterly |
| 3 | Engage employees in discussions about workplace policies and safety practices, giving them a sense of ownership and investment in their work environment. | HR Team | Monthly |
| 4 | Provide training for employees and managers to recognize signs of mental health issues and understand how to support colleagues who may be struggling. | Training Coordinator | Week 5-7 |
| 5 | Encourage an open and supportive culture where employees feel comfortable discussing mental health without fear of stigma or retribution. | HR Team | Ongoing |
| 6 | Acknowledge employees’ hard work and contributions regularly, boosting morale and cultivating a sense of belonging. | HR Manager | Week 4-8 |
| 7 | Provide access to confidential counseling services for employees facing personal or work-related challenges that may affect their mental health. | Occupational Health Team | Week 6-10 |
| 8 | Encourage team-building activities and social events that promote employee relationships, reducing feelings of isolation and promoting camaraderie. | Managers | Ongoing, bi-weekly |
| 9 | Promote policies encouraging a healthy work-life balance, such as flexible working hours, remote work options, and adequate vacation time. | HR Team | Monthly |
| 10 | Schedule workshops and resources on stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises. | Training Coordinator | Bi-annually |
| 11 | Promote physical wellness by providing gym memberships, organizing group fitness activities, or creating walking groups, as physical health is closely tied to mental well-being. | HR Team | Ongoing |
| 12 | Encourage employees to take regular breaks during workday to recharge and avoid burnout. | Managers | Ongoing |
| 13 | Ensure that there are clear, open lines of communication where employees can voice concerns, provide feedback, and report issues related to their mental well-being. | HR Manager | Ongoing |
| 14 | Ensure that workloads are manageable for all employees and make adjustments if employees are feeling overwhelmed. | Managers | Ongoing |
| 15 | Organize awareness campaigns that educate employees about mental health issues, available resources, and seeking help. | Managers | Ongoing |
| 16 | Integrate emotional intelligence principles (e.g., stress management, effective communication) into regular safety training programs. | Safety & Training Teams | Quarterly |
By implementing these actions, organizations can enhance their employees’ mental well-being, which will lead to better safety performance, reduced incidents, and a more positive workplace culture.
8. Utilize Ergonomic Solutions
Ergonomics is a crucial yet often overlooked aspect of workplace safety that can significantly enhance safety performance. By designing workspaces that accommodate the physical needs of employees, organizations can minimize the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and enhance overall productivity.
Ignoring ergonomic principles can lead to discomfort, fatigue, and injuries, ultimately affecting employee morale and safety outcomes. Investing in ergonomic solutions can promote a healthier work environment and demonstrate a commitment to employee well-being.
Here’s a list of actions to Improve Ergonomics in the Workplace:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Regularly evaluate workstations to identify ergonomic risks and make necessary adjustments tailored to individual employee needs. | HR Department/Ergonomics Specialist | Quarterly |
| 2 | Provide ergonomic workstations to reduce repetitive strain injuries. | Ergonomics Specialist & Procurement Team | Annually |
| 3 | Offer workshops or training sessions on proper body mechanics, lifting techniques, and workstation setup to educate employees on minimizing strain. | HR Department/Training Coordinator | Annually |
| 4 | Assess workstations to minimize physical strain and enhance comfort. Supply adjustable chairs, sit-stand desks, and ergonomic tools to support proper posture and reduce physical stress during work tasks. | Facilities Manager/Ergonomics Specialist | Ongoing |
| 5 | Promote a culture of taking regular breaks to stretch and move, alleviating tension and preventing fatigue from prolonged sitting or repetitive tasks. | HR Department/Health & Safety Team | Ongoing |
| 6 | Regularly gather input from employees about their comfort levels and any ergonomic concerns they experience to improve workplace design continuously. | Employee Engagement/HR Department | Biannually |
By taking these actions, organizations can significantly improve ergonomic conditions and ultimately improve health, safety, and environmental performance.
9. Promote Work-Life Balance
Promoting work-life balance is essential for enhancing safety performance in the workplace. When employees feel overwhelmed by excessive work demands, their focus and alertness diminish, increasing the likelihood of accidents and errors.
Organizations should encourage employees to take regular breaks and utilize their vacation time, enabling an environment where taking time off is a vital part of maintaining productivity and well-being.
Additionally, flexible work arrangements, such as remote work options or adjustable hours, can help employees better manage their personal responsibilities alongside their professional commitments.
Through the implementation of strategies for work-life balance, companies not only reduce the risk of burnout and stress-related issues but also cultivate a more engaged and resilient workforce, ultimately leading to improved safety outcomes and a stronger safety culture. Organizations can take several concrete actions to promote work-life balance:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Allow employees to adjust their start and end times to accommodate personal responsibilities, enabling them to manage their workloads effectively without sacrificing their well-being. | HR Manager | Ongoing |
| 2 | Implement comprehensive leave policies that cover various needs, such as parental leave, sick leave, and mental health days, ensuring employees can take the necessary time without the fear of negative repercussions. | HR Manager / Operations Manager | Ongoing/As Needed |
| 3 | Promote the importance of taking breaks and annual leave. Ensure employees utilize their vacation days to recharge, which can prevent burnout and enhance overall productivity. | HR Manager | Ongoing/Annually |
| 4 | Invest in wellness initiatives encouraging physical and mental health, such as fitness classes, meditation sessions, and stress management workshops. | HR Manager | Annually/As Needed |
| 5 | Promote a culture where managers regularly check in with employees to discuss workload, stress levels, and any support they need, creating an open dialogue about work-life balance. | HR Manager / Wellness Coordinator | Quarterly/Annually |
| 6 | Promote a culture where managers regularly check in with employees to discuss workload, stress levels, and any support they may need, creating an open dialogue about work-life balance. | Managers/HR Manager | Ongoing/Monthly |
| 7 | Encourage employees to disconnect after work hours and avoid emails or calls during personal time, reinforcing that time away from work is valuable. | Managers/HR Manager | Ongoing |
| 8 | Plan activities that allow employees to bond outside of work responsibilities, encouraging a sense of community that contributes to employee well-being. | Managers/HR Manager/Employee Engagement Team | Quarterly |
By implementing these actions, organizations can create a supportive environment that prioritizes work-life balance, ultimately improving safety performance and employee satisfaction.
10. Encourage Employee Involvement & Feedback
Promoting a culture of safety requires active participation from all employees, as their engagement is crucial to improving safety performance. One of the most effective ways to improve safety performance is by actively encouraging employee feedback. Employees are often the first to identify potential hazards or inefficiencies in safety protocols, and their insights can provide invaluable information for enhancing safety measures.
Creating a culture where employees feel comfortable sharing their observations and suggestions can significantly improve workplace safety. Organizations can implement regular feedback mechanisms, such as surveys, suggestion boxes, or open forums, to ensure that all voices are heard. It’s essential to collect this feedback and act upon it, demonstrating that the organization values employee input.
By encouraging employee involvement and acknowledging their feedback organizations can harness valuable insights, promote a sense of ownership, and enhance overall safety practices. In a collaborative environment where safety is a shared responsibility, organizations can enhance their safety performance by empowering their employees to take an active role in their own well-being. Here’s a list of actions to encourage employee involvement and feedback regarding workplace safety and health:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Offer ongoing training that not only covers safety protocols but also encourages employees to actively participate and share their experiences and feedback. | Team Leaders/SHE Manager | Annually / Ongoing |
| 2 | Implement anonymous feedback tools, such as whistle-blowing hotlines, where employees can voice safety concerns or suggest improvements without fear of repercussions. | Training Coordinator | Ongoing |
| 3 | Implement anonymous feedback tools, such as whistle blowing hotline, where employees can voice safety concerns or suggest improvements without fear of repercussions. | Worker Welfare Manager | Within 1 Month |
| 4 | Acknowledge individuals or teams who consistently demonstrate safe behaviors through incentives or recognition programs. | Managers | Quarterly |
| 5 | Promote an environment where employees feel comfortable discussing safety issues and can report hazards or near-misses without fear of judgment. | HR Team | Ongoing |
| 6 | Engage employees in identifying hazards and assessing risks in their work areas, leveraging their firsthand knowledge to enhance safety measures. | SHE Team | Monthly |
| 7 | Communicate that safety reporting will not result in negative consequences and that management values transparency and proactive reporting. | HR Team/Safety Committee | Quarterly |
| 8 | Establish a safety committee composed of representatives from various departments to evaluate feedback and recommend improvements. | Management Team | Within 2 Months |
| 9 | Ensure that every feedback submission receives a confirmation response, letting employees know their input has been recognized and valued. | Communications Team | Ongoing |
| 10 | Communicate the steps taken in response to feedback. Regularly update employees on how their input has influenced safety policies or practices. | Safety Committee | Monthly |
| 11 | Implement an incentive program that rewards employees for reporting safety concerns or participating in safety improvement initiatives. | HR Team | Annually |
| 12 | Hold regular team meetings focused on safety, allowing employees to voice concerns, share experiences, and suggest improvements in a supportive environment. | Team Leads | Monthly |
| 13 | Clearly communicate that safety reporting will not result in negative consequences and that management values transparency and proactive reporting. | Management Team | Ongoing |
| 14 | Integrate feedback sessions into regular safety training programs, encouraging employees to share thoughts on the training’s relevance and effectiveness. | Training Coordinator | During Scheduled Training |
| 15 | Distribute a regular safety newsletter that highlights safety topics, feedback received, and actions taken and encourages ongoing communication. | Senior Leadership/Safety Manager | Monthly |
| 16 | Distribute a regular safety newsletter that highlights safety topics, feedback received, actions taken, and encourages ongoing communication. | Communications Team | Bi-Monthly |
| 17 | Organize interactive workshops that specifically focus on gathering feedback and discussing safety improvements among employees. | Training Coordinator/HR Team | Annually |
By taking these steps, organizations empower their employees and cultivate a proactive safety culture with open communication that contributes to improved safety performance.
11. Safety Training and Education
Regular safety training and education are fundamental components in enhancing workplace safety performance. These programs should be tailored to address specific risks associated with the unique work environment and industry standards.
Incorporating hands-on training, simulations, and interactive workshops can make learning more engaging and relevant, promoting a deeper understanding of safety protocols. Moreover, retraining employees periodically helps reinforce critical safety practices and keeps everyone informed of new trends and regulations. Encouraging employee participation in these training sessions—whether through feedback mechanisms, safety champions, or incentive programs—can significantly elevate their commitment to a culture of safety.
Organizations can create a knowledgeable workforce by prioritising regular safety education that actively contributes to a safer work environment, ensures compliance with OSHA requirements and empowers employees with the knowledge to recognize hazards and respond effectively to reduce the likelihood of accidents significantly.
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Tailor training to specific workplace hazards and job functions, incorporating relevant scenarios. | Training Coordinator | 1 month |
| 2 | Educate employees on recognizing and responding to hazards effectively. | Safety Manager | Ongoing |
| 3 | Incorporate virtual training, simulations, and gamified learning experiences to engage employees. | IT Team and Training Team | 3 months |
| 4 | Enable training access via smartphones or tablets for on-the-go learning. | IT Team | 2 months |
| 5 | Define key markers of success in safety performance, such as reduction in incidents or increased training completion rates. | Safety Committee | Quarterly |
| 6 | Involve employees in the development and delivery of training to increase engagement and ownership. | Team Leads | Annually |
| 7 | Designate employees who will lead safety efforts and advocate for best practices among their peers. | Supervisors | 2 months |
| 8 | Implement continuous training programs rather than one-off seminars, including refresher courses to keep knowledge current. | HR/Training Coordinator | Quarterly |
| 9 | Practice emergency procedures and responses through drills to ensure preparedness. | Emergency Response Team | Biannually |
| 10 | Regularly ask for input on training content and safety practices to identify areas for improvement. | HR and Safety Committee | Annually |
| 11 | Measure the effectiveness of the training programs through incident reports, employee surveys, and safety audits. | Safety Compliance Officer | Quarterly |
| 12 | Regularly review and incorporate the latest safety practices and technologies into training programs. | Safety Manager | Annually |
By implementing these actions, organizations can create a robust safety training and education program that enhances safety performance and builds a culture of safety throughout the workplace.
12. Maintenance of Equipment and Tools
Ensuring the proper maintenance of equipment and tools is vital for creating a safe work environment. Regular inspections and maintenance not only prolong the lifespan of machinery but also significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries caused by malfunctioning or poorly maintained tools.
A proactive maintenance strategy involves adhering to scheduled checks, promptly addressing any identified issues, and keeping detailed records of repairs and maintenance activities. By prioritizing equipment upkeep, organizations can enhance operational efficiency while safeguarding their employees’ well-being.
Here’s a list of actions to ensure proper maintenance of equipment and tools:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Implement a routine maintenance schedule for all tools and equipment | Maintenance Supervisor | Within 1 Month |
| 2 | Conduct regular inspections to identify wear and tear or potential hazards | Safety Officer | Weekly/Monthly |
| 3 | Train employees on proper usage and maintenance techniques for equipment | Training Coordinator | Quarterly |
| 4 | Establish a reporting system for employees to notify management of any equipment issues | IT Department/HR Team | Within 2 Weeks |
| 5 | Keep detailed logs of maintenance activities, repairs, and replacements | Maintenance Team | Ongoing |
| 6 | Replace or repair any tools or equipment that do not meet safety standards | Procurement Manager | As Needed |
| 7 | Ensure that maintenance personnel are adequately trained and equipped to perform their tasks | Maintenance Supervisor | Annually |
| 8 | Utilize manufacturer guidelines and best practices for maintenance procedures | Maintenance Team | Continuous |
| 9 | Conduct 3rd party inspections and audits to ensure compliance with safety and industrial hygiene standards. | External Auditors & EHS Team | External Auditors & EHS Team / As Required |
By implementing these actions, organizations can ensure their tools and equipment are well inspected and tested, further contributing to safety performance throughout the workplace.
13. Adopt AI and Utilize Technology
Adopting artificial intelligence (AI) and leveraging technology in today’s rapidly evolving workplace can significantly enhance safety performance. AI-driven tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential hazards, enabling organizations to address risks before they result in incidents proactively.
Wearable technology, such as smart helmets and safety vests equipped with sensors, can monitor workers’ vital signs and environmental conditions in real-time, alerting them to potential dangers. Additionally, mobile applications can streamline communication about hazards, allowing employees to report unsafe conditions instantly and receive immediate feedback.
By integrating these innovative technologies into safety programs, organizations can promote a culture of safety that not only improves compliance with regulations but also empowers employees to take an active role in their wellbeing and that of their colleagues. This tech-enabled approach enhances situational awareness and reinforces the commitment to continuous improvement in safety performance.
Here’s a list of recommendations for adopting AI and utilizing technology in the context of safety, health, and environmental practices within organizations:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Use software that helps track compliance, incidents, and audits effectively. | IT Team/Safety Manager | Within 2 Months |
| 2 | Use AI algorithms to analyze historical safety data and identify patterns or trends that signal potential hazards. | Data Analytics Team | Quarterly Analysis |
| 3 | Utilize technology to automate monitoring compliance with safety regulations and internal protocols. This can include IoT sensors to track environmental conditions and workplace practices. | Procurement Department | Within 6 Months |
| 4 | Leverage virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) for training programs that simulate hazardous scenarios. | Training Coordinator/IT Team | Annually |
| 5 | Create or adopt mobile applications that allow employees to report safety issues or near-misses instantly. | App Development Team | Within 4 Months |
| 6 | Implement AI tools to conduct comprehensive risk assessments that evaluate workflows, employee behavior, and environmental conditions. | Safety Committee | Biannually |
| 7 | Employ drones or robots with cameras and sensors to conduct safety inspections in hard-to-reach areas. | IT Team/Safety Manager | Ongoing |
| 8 | Use technology platforms to create open channels for dialogue about safety concerns. This can include chatbots or forums where employees can discuss safety issues and share best practices. | HR Team/IT Team | Monthly |
| 9 | Utilize data visualization tools to present safety metrics and trends effectively. This can help management and employees understand the importance of safety and the impact of their behaviors. | Safety Manager/Data Team | Quarterly |
| 10 | Use IoT and AI to monitor equipment health and predict maintenance needs. | IT Team/Maintenance Department | Ongoing |
| 11 | Employ drones or robots equipped with cameras and sensors to conduct safety inspections in hard-to-reach areas. | Maintenance/Safety Teams | As Needed |
| 12 | Utilize technology to monitor environmental conditions, such as air quality or exposure to hazardous materials, in real-time. | Safety Officer | Ongoing |
| 13 | Use gamification techniques in safety training and practices to engage employees. Reward systems for safe behavior can enhance participation and commitment to a safety culture. | Training Coordinator | Annually |
| 14 | Adopt wearable devices that monitor health metrics (e.g., heart rate, fatigue levels) and safety metrics (e.g., exposure rates, proximity alerts) and provide alerts for potential health concerns. | HR Team/Safety Manager | Within 6 Months |
| 15 | Establish AI-powered systems that learn from incidents and continuously update safety protocols and training based on new data and insights. | IT Team/Data Science Team | Ongoing |
| 16 | Partner with technology companies and startups that focus on safety innovations to stay ahead in adopting the latest safety technologies and practices. | Procurement/Management | Annually |
| 17 | Implement mobile training applications to facilitate ongoing education and updates on safety procedures. | Training Coordinator/IT Team | Within 3 Months |
By implementing these recommendations, organizations can enhance their safety culture, reduce risks, and create a healthier work environment while embracing the potential of AI and technology.
14. Encourage Reporting of Safety, Health, and Environment Matters
Promoting an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting safety, health, and environmental (SHE) concerns is crucial for improving overall safety performance. When staff members are encouraged to speak up about potential hazards, near misses, or unsafe practices, organizations can address issues proactively rather than reactively.
This practice not only helps to identify and mitigate risks but also cultivates a culture of safety where everyone feels responsible for maintaining a safe workplace. To promote effective reporting, organizations can implement the following actions:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Allow anonymous reporting channels to help employees feel more secure in voicing their concerns without fear of reprisal. | SHE Manager/HR Team | Within 1 Month |
| 2 | Develop straightforward guidelines and a user-friendly platform for how employees should report SHE concerns, ensuring that these procedures are easily accessible and well-communicated. | Management Team | Ongoing |
| 3 | Conduct training sessions that educate employees on the importance of SHE reporting and how to identify potential hazards. | Training Coordinator | Quarterly |
| 4 | Provide regular updates to employees on the outcomes of reported concerns and the actions taken, reinforcing the value of their input. | Safety Committee/Communications Team | Monthly |
| 5 | Create incentive programs to recognize employees who actively report safety concerns, promoting a proactive safety culture. | HR Team | Annually |
| 6 | Ensure the process is accessible and encourages prompt reporting | HSE Manager | Immediately |
| 7 | Allow for anonymous reporting channels to help employees feel more secure in voicing their concerns without fear of reprisal. | HR Manager/SHE Manager | Within 2 Months |
| 8 | Use posters and digital displays throughout the workplace to remind employees of the importance of reporting safety concerns and how to do so effectively. | Communications Team/SHE Team | Within 2 Weeks |
By implementing these actions, organizations can facilitate open communication about safety matters, leading to a more informed and engaged workforce that actively participates in improving safety performance.
15. Implement a Rewards and Recognition System
Establishing a rewards and recognition system is a powerful strategy to enhance safety performance within the workplace. This system not only motivates individuals to adhere to safety protocols but also promotes a culture of accountability and proactive behavior.
By acknowledging and rewarding employees for their commitment to safety, you cultivate an environment where safety is prioritized and valued. To effectively implement this system, consider the following actions:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Offer rewards to employees who complete safety training and demonstrate their understanding of protocols and commitment to emergency preparedness. | HR Team/Training Coordinator | Monthly |
| 2 | Provide incentives for regular attendance at safety meetings, reinforcing their importance in maintaining a safe workplace. | HR Team/Safety Manager | Monthly |
| 3 | Encourage employees to report near-misses by recognizing those who take the initiative to highlight potential hazards. | Safety Manager | Ongoing |
| 4 | Reward individuals or teams that consistently inspect and maintain tools and machinery, ensuring they are safe for use. Recognize and reward teams or individuals who consistently maintain high standards of hygiene. | Maintenance Department/Safety Team | Quarterly |
| 5 | Offer recognition for employees who display safe behaviors, such as proper lifting techniques and adherence to safety guidelines. | Supervisors/HR Team | Ongoing |
| 6 | Establish a program where employees can nominate their peers for exemplary safety practices, encouraging camaraderie and shared responsibility for safety. | HR Team | Biannually |
| 7 | Implement a recognition program that rewards employees for demonstrating safe practices and contributing to a safe work environment. | HR Team/Safety Committee | Quarterly |
| 8 | Create a Safety Champion Program to celebrate safety milestones and encourage continuous improvement. | Safety Manager/HR Team | Annually |
By implementing these actions, you will not only reinforce safe behaviors but also engage employees in a more meaningful way, ultimately leading to a safer and more productive workplace.
16. Conducting Regular Safety Inspections and Audits
Regular safety inspections are a cornerstone of effective organisational safety performance management. These inspections help assess current workplace conditions and serve as a valuable tool for tracking compliance with safety regulations and identifying any weaknesses within departments.
Implementing formal safety audits and informal spot-checks ensures a comprehensive evaluation of safety protocols tailored to the specific risks associated with different industries. Moreover, promoting a culture where employees understand the importance of these inspections encourages them to participate actively in safety monitoring, ultimately leading to a safer and more health-conscious workplace.
By prioritising regular safety inspections, organizations can proactively identify and address potential hazards significantly before they escalate into serious incidents, enhance employee well-being, and demonstrate their commitment to creating a safety culture. To effectively implement Safety Inspections and Audits, consider the following actions:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Create a calendar for regular inspections, specifying frequency based on the type of workplace and identified risks (e.g., weekly, monthly, quarterly). | Safety Manager | After corrective actions have been implemented, follow-up inspections will be conducted to verify that issues have been resolved and to evaluate the effectiveness of the changes. |
| 2 | Develop detailed checklists tailored to specific areas and tasks within the workplace, ensuring they align with OSHA standards and industry requirements. | Safety Officer & Maintenance Officer | Within 2 Months |
| 3 | Provide training for individuals responsible for conducting inspections, focusing on identifying hazards, using checklists, and understanding compliance requirements. | Training Coordinator | Quarterly |
| 4 | Carry out both formal and informal inspections. Formal inspections should adhere to the established schedule, while informal inspections can be spontaneous to ensure ongoing safety vigilance. | Department Supervisors | Ongoing |
| 5 | Involve employees in the inspection process. Their firsthand experience can provide valuable insights into potential hazards and underlying issues. | Team Leads/Safety Champions | Quarterly |
| 6 | Keep thorough records of all inspections, noting any hazards identified, corrective actions taken, and any recommendations for improvement. | Compliance Team | Ongoing |
| 7 | Share findings from inspections with all staff members. This transparency helps reinforce the importance of safety and ensures everyone is aware of potential hazards. | Communications Team | Monthly |
| 8 | Based on inspection findings, prioritize corrective actions based on severity and potential risk to employees. Ensure that urgent issues are addressed promptly. | Safety Manager | Immediate (within 1 Week for urgent issues) |
| 9 | Consider using digital tools or software to streamline the inspection process, making documenting findings and tracking corrective actions easier. | Safety Officer | Within 1 Month Post-Correction |
| 10 | Regularly review and update safety protocols and policies based on inspection findings and new regulations to ensure continuous improvement in safety performance. | Safety Committee | Quarterly |
| 11 | Regularly analyze inspection and audit data to identify trends, recurring issues, or improvement areas. Use this data to inform training and safety initiatives. | IT Department | Within 3 Months |
| 12 | Create an open dialogue where employees can provide feedback or suggest improvements related to safety inspections. | HR and Team Leads | Ongoing |
| 13 | Schedule formal internal and 3rd Party safety audits that involve comprehensive evaluations of safety practices to ensure compliance with safety and industrial hygiene standards. Ensure these audits are well-documented and actionable. Conduct 3rd party inspections and audits. | External Auditors/Safety Manager | Annually |
| 14 | Regularly analyze inspection and audit data to identify trends, recurring issues, or areas needing improvement. Use this data to inform training and safety initiatives. | Safety Compliance Officer | Quarterly |
| 15 | Promote a workplace culture where safety is prioritized, and employees are encouraged and rewarded for participating in safety inspections and voicing concerns. Ensure audits cover all areas of the workplace and involve employee feedback. | Management Team | Ongoing |
By implementing these actions, organizations can enhance their safety performance, reduce risks, and create a safer work environment for all employees.
17. Establish Emergency Preparedness and Emergency Response
To enhance safety performance, it is crucial to establish robust emergency preparedness and response plans that are well-documented and accessible to all employees. This involves conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential emergencies specific to the workplace, followed by developing tailored response strategies.
Regular training drills should ensure that employees are familiar with emergency procedures, roles, and communication protocols, allowing for a swift and organized response in real emergencies.
Additionally, equipping designated emergency response teams with the necessary tools and resources, such as first aid kits and communication devices, will strengthen the organization’s preparedness.
Engaging employees in the planning process not only encourages a safety culture but also empowers them to act confidently during crises, ultimately minimizing risks and protecting the well-being of all personnel.
To establish emergency preparedness and improve emergency response to enhance overall safety performance, organizations can implement the following actions:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Regularly identify and evaluate potential hazards within the workplace to establish what emergencies could arise. | Safety Officer/Emergency Response Team | Annually/As Needed |
| 2 | Create comprehensive emergency response plans tailored to the identified risks, including procedures for evacuation, communication, and medical assistance. | Safety Officer/Management | Annually/As Needed |
| 3 | Organize regular training sessions and emergency drills for all employees to ensure they understand the emergency procedures and can respond effectively under pressure. | Training Team/Safety Officer | Biannually/Annually |
| 4 | Implement Virtual Reality (VR) simulations to provide hands-on training experiences for employees, allowing them to practice emergency responses in a safe, controlled environment. | Training Team/IT Department | Annually/As Needed |
| 5 | Ensure there are clear protocols for communication during an emergency, including designating individuals responsible for relaying information and instructions. | Safety Officer/HR | Quarterly/As Needed |
| 6 | Maintain updated lists of emergency contacts, including local emergency services, internal emergency response teams, and key personnel within the organization. | Safety Officer/HR | Quarterly |
| 7 | Identify and communicate safe assembly points where employees should gather in an emergency, ensuring everyone knows where to go. | Facilities Team/Safety Officer | Annually/As Needed |
| 8 | After any emergency or drill, analyze the response to identify strengths and areas for improvement, updating emergency procedures as necessary. | Safety Officer/Facilities Team | Annually/As Needed |
| 9 | Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of emergency response procedures and make necessary updates to reflect changes in operations, personnel, or identified risks. | Safety Officer/Emergency Response Team | Quarterly/After Drills |
| 10 | Involve employees in developing and reviewing emergency preparedness plans, as they can provide valuable insights based on their experiences and observations. | Safety Officer/Emergency Response Team | After Every Drill/Incident |
| 11 | Provide resources and training on stress management and psychological first aid, preparing employees mentally for emergencies and enhancing their ability to respond calmly. | HR/Training Team | Annually/As Needed |
| 12 | Involve employees in the development and review of emergency preparedness plans, as they can provide valuable insights based on their experiences and observations. | Safety Officer/HR | Ongoing/Annually |
By executing these actions, organizations can significantly enhance their emergency preparedness and response capabilities, leading to improved safety performance and a stronger safety culture.
18. Incident Investigation, Case Study, and Follow-Up
Effective incident investigation is a cornerstone of any robust safety management system, serving as a critical tool for understanding the root causes of workplace incidents and preventing future occurrences. The process involves systematic data collection, analysis, and formulating actionable recommendations.
A well-executed investigation not only addresses the immediate aftermath of an incident but also reinforces an organization’s commitment to continuous improvement in safety practices.
Incident investigations are not merely a regulatory requirement but an essential practice for advancing workplace safety. By learning from past incidents and implementing recommendations effectively, organizations can promote a culture of safety and accountability, ultimately safeguarding their employees and operations
Here’s a list of actionable items for incident investigation and follow-up to improve safety performance in the workplace:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Assign a dedicated team to investigate incidents as soon as they are reported | Incident Response Coordinator | IT Department, in collaboration with Safety Manager |
| 2 | Gather evidence and witness statements shortly after the occurrence | Investigation Team | Within 48 hours of the incident |
| 3 | Implement digital solutions to streamline the reporting, investigation, and tracking of incidents | Ensure all employees are aware of the outcomes and implications of safety protocols | Within 3 months |
| 4 | Involve employees in the investigation process to encourage ownership and accountability | Investigation Team Lead | During the investigation phase (within 1 week of the incident) |
| 5 | Encourage feedback and insights from coworkers who are familiar with the work environment | Department Heads / Team Leaders | During the investigation phase (within 1 week of the incident) |
| 6 | Use techniques like the “5 Whys” or Fishbone Diagram to identify underlying issues contributing to the incident | Investigation Team | Within 1 week of incident analysis |
| 7 | Analyze data to detect patterns or recurring hazards | Data Analyst or Safety Team | Monthly |
| 8 | Maintain thorough records of investigations, findings, and any corrective actions taken | Safety Administrator / Document Control Officer | Ongoing (complete within 1 week of investigation closure) |
| 9 | Share findings with all relevant stakeholders to promote transparency | Safety Manager | Within 1 week of investigation closure |
| 10 | Hold safety meetings to discuss the findings of the incident investigation | Safety Committee or HR | Monthly or as incidents occur |
| 11 | Ensure all employees are aware of the outcomes and implications for safety protocols | Training Coordinator or Safety Manager | During the next team meeting or within 2 weeks of investigation closure |
| 12 | Develop and prioritize actionable steps to address identified risks | Safety Manager in collaboration with Department Heads | Within 2 weeks of investigation closure |
| 13 | Assign responsibilities and set deadlines for completion of corrective actions | Safety Manager | Immediately after corrective actions are identified (within 1 week) |
By implementing these actionable items, organizations can enhance their incident investigation processes and encourage a proactive approach to improving workplace safety performance.
19. Monitor and Measure Performance
Monitoring and measuring safety performance is essential for identifying trends, understanding safety initiatives’ effectiveness, and pinpointing improvement areas. Organizations should implement a systematic approach to collecting data on safety-related events, such as incidents, near misses, and safety audits.
Utilizing key performance indicators (KPIs) tailored to specific organizational goals can provide insights into how well safety protocols are followed and where gaps may exist. Regularly reviewing this data allows management to assess whether performance is improving, stagnating, or declining, enabling timely interventions.
Here’s a list of actions to monitor and measure the performance of Safety, Health and Environment:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Implement a system to track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to safety and health, such as incident rates, near-miss reports, and safety training completion rates. | Safety Manager/Safety Committee | Monthly |
| 2 | Track the safety and environmental audits and inspections to ensure compliance with established safety standards. | Review and update safety protocols and performance metrics based on incident analysis and employee feedback. | Quarterly |
| 3 | Analyze workplace incidents and near-misses to identify trends, root causes, and areas of improvement. | Safety Analyst/HR Team | Monthly |
| 4 | Track employee participation in safety training and meetings, and measure safety behaviors and compliance improvements. | Safety Manager/HR Department | Quarterly |
| 5 | Use digital tools to monitor real-time safety data, such as environmental conditions (e.g., air quality, noise levels) and employee health metrics (e.g., fatigue, heart rate). | IT Department/Safety Team | Ongoing |
| 6 | Track employee participation in safety training and meetings, and measure improvements in safety behaviors and compliance. | HR Department/Training Coordinator | Monthly |
| 7 | Hold regular safety performance reviews with team leaders and department heads to discuss safety progress and challenges. | Safety Manager/Department Heads | Biannually |
| 8 | Use surveys and feedback forms to gather employee opinions on safety practices, training, and overall workplace health. | HR Department/Safety Team | Annually |
| 9 | Monitor the effectiveness of corrective actions taken after incidents or audits to ensure they result in improved safety outcomes. | Safety Manager/Department Heads | Ongoing |
| 10 | Conduct periodic health and safety culture assessments to ensure employees feel supported and safety is a top priority. | HR Department/Employee Engagement Team | Annually |
| 11 | Implement an environmental monitoring system to track air quality, water usage, waste management, and energy consumption. | Environmental Officer/Sustainability Team | Monthly |
| 12 | Analyze trends in environmental performance, focusing on resource consumption, waste generation, and emissions, to identify opportunities for sustainability improvements. | Environmental Analyst/Management Team | Monthly |
| 13 | Review and update safety, health and environmental policies and procedures to integrate best practices, technological advancements, and legal compliance. | Environmental Officer/Compliance Officer | Quarterly |
| 14 | Analyze trends in occupational health performance, focusing on employee health metrics, absenteeism, injury rates, and the impact of workplace health programs. | Occupational Health Analyst/Management Team | Monthly |
| 15 | Review and update occupational health policies and procedures to integrate best practices, new technologies, and legal compliance related to employee health. | Occupational Health Officer/Compliance Officer | Quarterly |
Regularly evaluate safety performance to measure progress toward safety goals. By tracking these lagging indicators, organizations can assess the effectiveness of their safety, health, and environmental programs and identify areas for improvement to prevent future incidents.
20. Regularly Review and Update Safety Policies and Procedures
To develop a safety culture and continuously enhance safety performance, organizations must prioritize regularly reviewing and updating their safety policies and procedures. This process ensures that the policies remain relevant and effective in addressing current risks and compliance requirements.
Engaging employees in these reviews is crucial, as their firsthand experiences can provide valuable insights into practical challenges and potential improvements.
Furthermore, updating safety policies in response to new regulations, advancements, or changing workplace dynamics demonstrates a commitment to safety that can motivate employees to participate in safe work practices actively.
Organizations can identify gaps or weaknesses that compromise employee safety and operational efficiency by systematically evaluating safety procedures. Ultimately, a proactive approach to reviewing and refining safety policies safeguards employees and enhances overall organizational performance and resilience.
To regularly review and update safety policies and procedures and improve safety, health and environmental performance, organizations can implement the following actions:
| Sr # | Action | Responsible | Timeline |
| 1 | Review and update safety protocols and performance metrics based on incident analysis and employee feedback. | Compliance Team | Quarterly |
| 2 | Review and update safety protocols and performance metrics based on incident analysis and feedback from employees. | Safety Manager/HR Department | Quarterly |
| 3 | Review any changes in local, state, or federal safety regulations and ensure policies are updated accordingly. Review any outdated practices in existing policies. | Legal/Compliance Officer | Ongoing (every 6 months) |
| 4 | Designate specific team members or a safety committee to oversee the review process and ensure accountability. | Safety Committee Chairperson | Monthly |
| 5 | Automate compliance tracking and reporting to reduce administrative burdens and enhance accuracy. | Software Administrator | 4 months |
| 6 | Maintain liaison with local regulatory bodies to stay informed about changes in safety regulations. | Compliance Officer | Ongoing |
| 7 | Benchmark against industry standards. Compare your safety policies against industry standards and best practices to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement. | External Auditor/Consultant | Annually |
| 8 | Keep thorough records of all reviews and updates to safety policies and ensure that these documents are easily accessible to all employees. | Document Controller | As required |
| 9 | Regularly solicit input through surveys or manager one-to-ones to identify new areas for improvement | HSE Manager | Quarterly |
| 10 | After implementing updates, continuously monitor their impact on safety performance through KPIs and employee feedback. | HSE Manager | Ongoing |
Implementing these actions will help create a proactive approach to safety management, improving safety performance across the organization.
Conclusion: The Importance of Continual Improvement in Safety Performance
Improving safety performance in the workplace is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that requires commitment from both employers and employees. By continuously evaluating and enhancing safety measures, businesses can create a work environment that minimises accidents and promotes overall well-being and productivity.
The pursuit of safety is intrinsically linked to operational excellence. Companies that prioritize safety and integrate it into their core business practices can see improvements in employee morale, risk management, and financial performance.
Safety should be viewed as a shared responsibility, where open communication, training, and engagement among all levels of staff become pivotal to success.
Moreover, acknowledging the need for continual improvement in safety performance helps organizations adapt to changing circumstances, be it new regulations, technological advancements, or shifts in workforce dynamics. This adaptability promotes resilience, enabling businesses to navigate challenges effectively while ensuring the safety of their employees.
In summary, organizations that commit to a culture of continual safety improvement are not merely adhering to rules; they are investing in their workforce and setting a foundation for long-term success. A safe workplace is productive, and prioritizing safety should be a staple in every business’s strategy moving forward.
References:
https://www.osha.gov/safety-management/program-evaluation
Join Our Safety Community!
Stay informed with the latest tips and insights on occupational health, safety, and the environment.




A sincere thank-you for your time and thoughtfulness. We deeply appreciate your efforts!
You’re very welcome! I’m so glad you found the post helpful. I appreciate your kind words and hope you can implement some of the suggestions to improve safety performance in your workplace further.