Introduction:
Health and safety are essential aspects of any workplace, whether it is an office, a factory, a construction site, or a hospital. Health and safety refer to workers’ physical, mental and emotional well-being and preventing accidents, injuries, illnesses, and fatalities that may occur due to work-related activities. To answer the question of why is it important to manage health and safety, we will explore the four main reasons why health and safety should be a priority in every workplace. These are moral reasons, financial reasons, legal reasons, and sustainability reasons.
What is health and safety?
Health and safety, often abbreviated as H&S, refers to principles, guidelines, and practices aimed at protecting individuals’ physical, mental, and emotional well-being in various environments, particularly in workplaces. It involves identifying and mitigating risks, promoting a safe working culture, and complying with relevant laws and regulations.
What is health and safety Management?
A health and safety management system is a set of policies, procedures, and practices that aim to prevent or reduce the risk of injury, illness, and death in the workplace. A HSMS is based on the principle of continuous improvement, which means that it is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the work environment, legal requirements, and best practices.
A well-designed and implemented health and safety management system can provide many benefits for the organization, such as reducing injuries and illnesses, improving productivity and quality, enhancing reputation and customer satisfaction, complying with legal requirements, or saving costs. However, it requires continuous effort and commitment from all levels of the organization to achieve these benefits. Therefore, it is important to have a clear vision of what you want to achieve with your HSMS, a realistic plan of how to get there, a dedicated team of people who can make it happen, and a regular review of your progress and performance.
Health and safety management also involves complying with relevant laws and regulations, implementing best practices, and promoting a positive safety culture. Effective health and safety management requires the commitment of everyone in the organization, from top management to frontline workers. It also requires a systematic approach that includes the following steps:
- Policy: This is a statement of the organization’s commitment to health and safety, as well as its goals and objectives. It also defines the roles and responsibilities of managers, supervisors, workers, and other stakeholders.
- Planning: This involves identifying the hazards and risks associated with the work activities and developing strategies to eliminate or control them. It also includes setting performance indicators, targets, and action plans to measure and improve health and safety outcomes.
- Implementation: This involves putting the policies and plans into action by providing adequate resources, training, communication, supervision, documentation and establishment of operational controls and emergency procedures. It also ensures that workers are involved and consulted in health and safety matters and have the right to refuse unsafe work.
- Evaluation: This involves monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of the HSMS by conducting audits, inspections, investigations, and analyses. It also involves reporting on the results, taking corrective actions, and recognizing achievements.
- Audit and review: This is the periodic and systematic evaluation of the health and safety management system against the policy, objectives and standards, and the identification of strengths, weaknesses and opportunities for improvement.
- Continual Improvement: This involves using the evaluation results to identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance the HSMS performance. It also involves seeking new opportunities for innovation and learning from best practices or benchmarks. A good continual improvement process should be driven by a proactive and positive attitude that embraces change and seeks excellence. It should also be integrated with the organization’s strategic planning and business objectives.
How can you manage health and safety in your workplace?
Many resources are available to help organizations manage health and safety, including government agencies, professional organizations, and training providers. Here are some examples of health and safety management activities. However, some of the common steps that you can take are:
- Establish a health and safety policy that defines your goals, responsibilities, procedures, and resources for health and safety management.
- Conduct a health and safety risk assessment that identifies the hazards and risks that may affect your workers’ health and safety in the workplace.
- Implement health and safety measures that eliminate or control the hazards and risks that you have identified, such as providing personal protective equipment (PPE), training, supervision, signage, emergency plans, etc.
- Monitor and review your health and safety performance regularly to ensure that your measures are effective, up-to-date, and compliant with the legal requirements.
- Communicate and consult with your workers, customers, suppliers, contractors, regulators, and other stakeholders on health and safety matters to raise awareness, obtain feedback, resolve issues, and promote cooperation.
By managing health and safety, businesses can reduce the financial costs of accidents and injuries. This can improve the bottom line and make the business more competitive. Here are some specific examples of how businesses can manage health and safety to reduce costs:
- Implement safety policies and procedures: This can help to prevent accidents and injuries from happening in the first place.
- Provide training to workers on safety topics: This can help workers identify hazards and take steps to protect themselves from harm.
- Inspect and maintain equipment and facilities: This can help to identify and repair potential hazards before they cause accidents or injuries.
- Investigate accidents and incidents: This can help to identify the root causes of accidents and injuries so that steps can be taken to prevent them from happening again.
The specific activities that organizations must undertake will vary depending on their operations’ size, nature, and complexity. However, all organizations should have a basic health and safety management system in place to protect their workers from harm. Organizations can protect their workers from harm by implementing a comprehensive health and safety management system and promoting their overall health and well-being.
Workers have a right to a safe and healthy workplace, which is the right thing to do to protect them from harm.
What are the four reasons to manage health and safety at work?
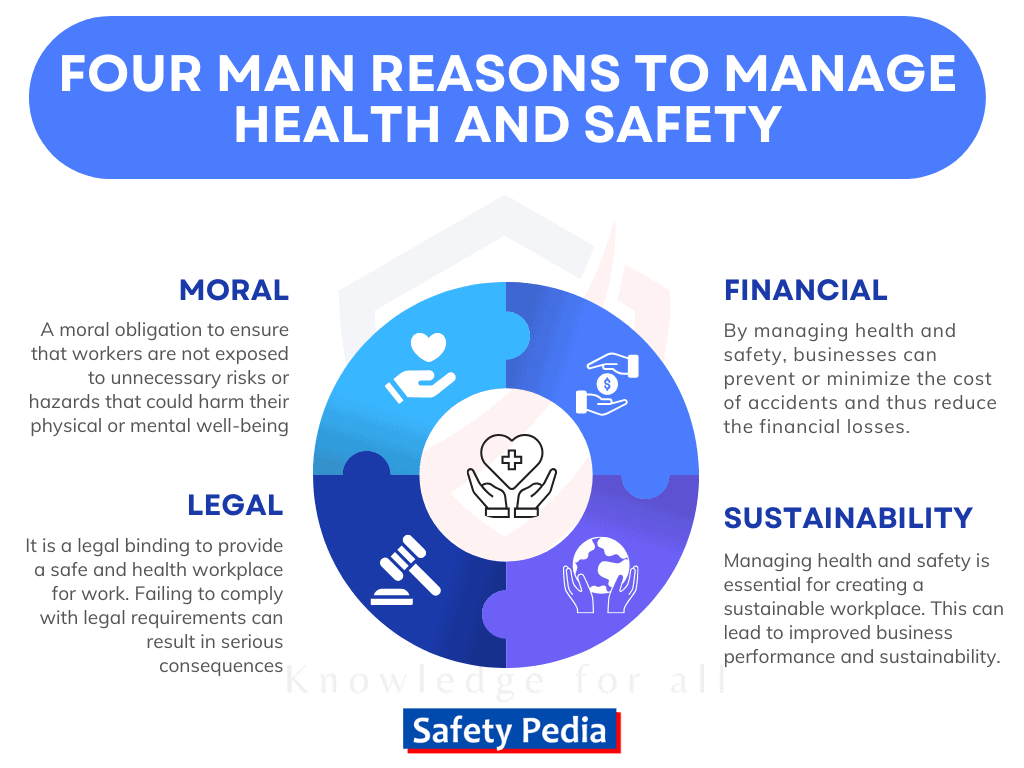
There are many reasons why health and safety should be a priority for employers and employees alike. However, the four main reasons are:
Moral Reasons:

One primary reason for implementing occupational health and safety measures is based on moral grounds. This means that employers and managers are morally obligated to ensure their workers are not exposed to unnecessary risks or hazards that could harm their physical or mental well-being. Workers, in turn, have a moral right to demand and expect a work environment that is safe and conducive to their health. By fulfilling this moral duty, employers and managers are complying with the law and demonstrating respect and care for their workers as human beings.
No one should go to work and risk being injured or killed. Workers should be able to focus on their jobs without worrying about their safety. Health and safety management helps ensure that workplaces are safe and workers are protected from harm. The moral reasons for health and safety management are the most important ones.
Protection of human life: The most important reason to manage occupational health and safety is to protect human life. Every employee has the right to work in a safe environment, and employers have a moral obligation to provide it. Workers have the right to work in an environment that does not compromise their health or safety, and employers have a duty to provide such an environment.
Ethical Responsibility: Employers have an ethical responsibility to provide a safe workplace for their employees. They should prioritize employee safety and ensure the working environment is safe for employee well-being.
Social responsibility: Employers must consider the impact of their operations on society as a whole. Providing a safe and healthy working environment can contribute to society’s well-being and reduce the negative impact of work-related accidents and illnesses. No one in society wants incidents or accidents; rather, they demand health and safety management. Occupational hazards can also affect the general public. For example, an accident in a chemical plant could cause an environmental disaster that affects nearby local communities. Effective OHS management can help prevent such incidents.
No one in society wants incidents or accidents; rather, they demand health and safety management.
Financial or Economic Reasons:

Another primary reason to manage health and safety is the financial savings that businesses can achieve. When exposed to hazards, workers may suffer injuries, illnesses, or property damages that affect their productivity and performance. Moreover, businesses may have to pay for medical bills, compensation claims, rehabilitation costs, and legal fees. These costs can be significant and impact the profitability and reputation of the business. Therefore, by implementing effective health and safety measures, businesses can prevent or minimize the occurrence of accidents and injuries and thus reduce the financial losses associated with them.
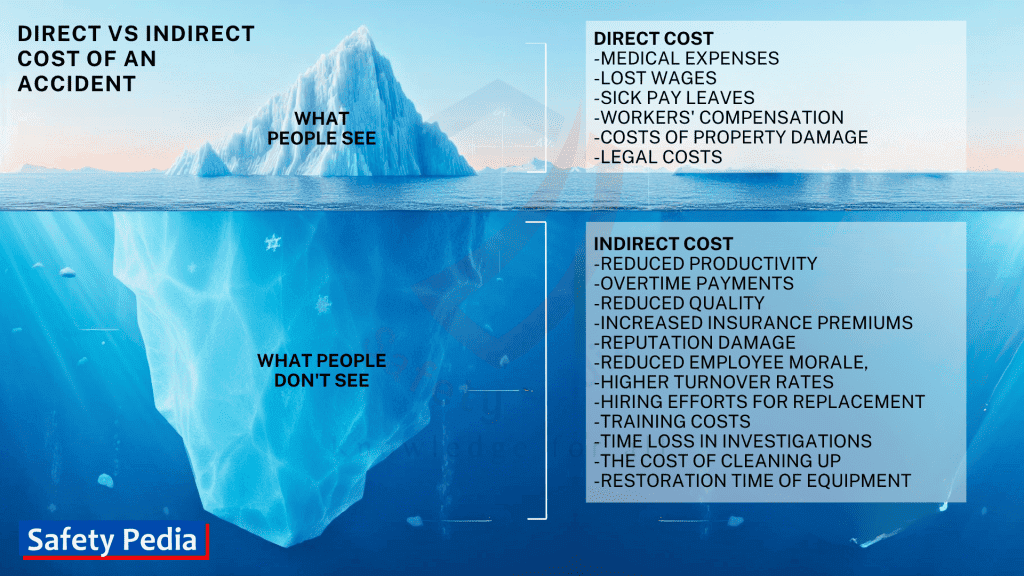
What are the direct and indirect costs of an accident at the workplace?
The direct and indirect costs of a workplace accident can be significant, both for the employee and the employer.
Direct Cost
The direct costs of a workplace accident are the costs that can be directly attributed and easily measured to the accident. See the table.
Indirect Cost
The indirect costs of a workplace accident are the hidden costs that cannot be directly attributed and are difficult to measure to the accident but are caused by the accident. See the table.
- Medical expenses, such as doctor’s visits, hospital stays, rehabilitation and surgery
- Lost wages for the injured employee or disability
- Sick pay leaves
- Workers’ compensation payments
- Costs of property damage, such as raw materials, repairs, or replacement of equipment and facilities
- Legal costs, if the injured employee sues the employer
- Reduced productivity due to absenteeism and lost work time
- Additional workloads on existing employees to cover the production loss
- Overtime payments
- Reduced quality
- Increased insurance premiums
- Damage to the company’s reputation
- Reduced employee morale,
- Higher turnover rates
- Hiring efforts to replace workers
- Cost of implementing new safety measures, equipment
- Training costs for temporary or permanent replacements
- Time lost while going through investigations and reporting
- The cost of cleaning up, especially if it involves hazardous materials
- Restoration time of equipment to efficiency
What are the insured and uninsured costs of an accident at the workplace?
In the context of workplace accidents, some costs may be insured, and those that are typically uninsured. Here’s an overview of both:
Insured Costs
The insured costs of a workplace accident are the costs that are covered by the employer’s insurance policy. See the table.
Uninsured Costs
The uninsured costs of a workplace accident are the costs that are not covered by the employer’s insurance policy. See the table.
- Medical expenses
- Lost wages
- Workers’ compensation payments, such as disability benefits
- Costs of property damage
- Liability Insurance (If a workplace accident involves third parties, such as contractors or visitors, liability insurance can cover legal expenses, settlements, or judgments related to third-party claims)
- Property Insurance
- Business Interruption Insurance
- Reduced productivity due to absenteeism and lost work time
- Increased insurance premiums
- Damage to the company’s reputation
- Reduced employee morale and Productivity Loss
- Costs of retraining replacement workers
- Deductibles for workers’ compensation or liability claims
- Training and Prevention Costs
- Regulatory Fines imposed by regulatory authorities
It’s crucial for employers to understand the scope of insurance coverage and uninsured costs associated with workplace accidents. Companies can focus on prevention, safety programs, employee training, and creating a safety culture to mitigate these uninsured costs. By doing so, they can reduce the risk of accidents and minimize the financial and human toll associated with workplace incidents.
By managing occupational health and safety, companies can reduce these costs and improve their performance. The total cost of a workplace accident can vary depending on many factors, such as the severity of the injury, the type of industry, and the company’s size. However, even minor accidents can have a significant financial impact on both employees and employers.
By investing in health and safety management, businesses can save money in the long run.
Legal Reasons:

Another primary reason why employers need to take health and safety seriously is the legal implications of neglecting or violating them. Some various laws and regulations set the standards and obligations for employers to protect their workers and the public from harm. If employers fail to meet these requirements, they can face serious consequences, such as fines, penalties, and even imprisonment, depending on the severity of the breach. Therefore, employers should be aware of their legal responsibilities and comply with them diligently.
Some several laws and regulations require employers to manage health and safety. These laws and regulations vary from country to country, but they generally require employers to provide a safe and healthy workplace for their employees.
Some examples of laws and regulations that require employers to manage health and safety include:
- The Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) in the United States
- The Health and Safety at Work Act (HSWA) in the United Kingdom
- The Canada Occupational Safety and Health Act (COSH)
- The Australian Work Health and Safety Act (WHS Act)
- The European Union’s Framework Directive on Safety and Health at Work
Employers who fail to comply with these laws and regulations can face several consequences, including:
- Fines and penalties
- Imprisonment
- Civil lawsuits from injured workers
- Increased insurance premiums
- Damage to their reputation
Compliance: Employers must legally comply with occupational health and safety regulations. Failure to comply can result in fines, legal action, and reputational damage.
Legal Liability: Employers can be liable for work-related injuries or illnesses. This includes compensation claims and legal action brought by injured employees or their families.
Reputation: Failure to manage occupational health and safety can damage a company’s reputation, which can have a negative impact on its ability to attract and retain employees, customers, and investors.
Overall, effective OHS management is an important part of responsible business practice and is crucial for the well-being of workers, companies, and society as a whole. Therefore, many organizations obtain certification in occupational health and safety management system ISO 45001 to manage health and safety.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to managing health and safety in the workplace.
Sustainability Reasons:

Another primary reason to manage health and safety is to promote sustainable development. Sustainable development is defined as “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” By managing health and safety, organizations can reduce the negative impacts of their activities on the environment, society, and economy. Managing health and safety also contributes to the well-being and productivity of workers, which are essential for achieving economic growth and social justice. Therefore, managing health and safety is a legal and moral obligation and a strategic and competitive advantage for organizations that want to thrive in a changing world.
Managing health and safety is essential for creating a sustainable workplace. When workers are healthy and safe, they are more productive and engaged. This can lead to improved business performance and sustainability.
SDGs with goals towards workplace safety
According to the International Labor Organization (ILO) estimates, approximately 2.3 million workers lose their lives annually due to work-related injuries and diseases. Furthermore, an additional 160 million workers suffer from non-fatal work-related illnesses, while 313 million suffer non-fatal injuries yearly. The economic impact on companies and economies is substantial, with the ILO projecting that work-related injuries and diseases lead to a loss equivalent to more than 4 percent of the world’s annual GDP.
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being aims to “substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination.”
Good Health 3.9, By 2030, substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water, and soil pollution and contamination. 3. a, strengthen implementation of the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control in all countries as appropriate. This target is also important for workplace safety, as it recognizes that exposure to hazardous chemicals and other pollutants can lead to serious health problems for workers.
SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth includes a target to “promote safe and secure working environments for all workers, including migrant workers, in particular women migrants, and those in precarious employment.”
SDG 16: Peace and Justice 1, 16.6 Develop effective, accountable, and transparent institutions at all levels
This target is important because it recognizes that workplace safety is essential for sustainable development. When workers are safe and healthy, they are more productive and engaged. This can lead to improved economic growth and poverty reduction.
Yes, sustainability is another primary reason to manage health and safety. A sustainable workplace is safe and healthy for workers and that minimizes its environmental impact. Managing health and safety is essential for creating a sustainable workplace.
Here are some specific examples of how managing health and safety can contribute to sustainability:
- Reduced environmental impact: Accidents and injuries can lead to environmental damage, such as chemical spills and air emissions. By managing health and safety, businesses can reduce their environmental impact and protect the planet.
- Promoting employee well-being: Employees who are healthy and safe are more likely to be productive and engaged. This can lead to improved business performance and sustainability.
- Attracting and retaining employees: Employees are more likely to work for businesses that are committed to health and safety. This can help businesses to attract and retain the best talent.
- Improved efficiency: When businesses invest in health and safety, they are more likely to have efficient operations. This is because employees are less likely to be absent from work due to illness or injury, and they are more likely to be able to focus on their work and perform their tasks to a high standard.
Managing health and safety is essential for creating a sustainable workplace. When workers are safe and healthy, they are more productive and engaged. This can lead to improved business performance and sustainability. By managing health and safety, businesses can create a more sustainable workplace. This can benefit the business, its employees, and the environment. Here are some specific examples of how businesses can manage health and safety to promote sustainability:
- Reduce the use of hazardous chemicals: Businesses can reduce their use of hazardous chemicals by substituting them with safer alternatives. This can help to reduce the risk of accidents and injuries and to protect the environment.
- Improve energy efficiency: Businesses can improve their energy efficiency by making changes to their operations and equipment. This can help to reduce their environmental impact and save money on energy costs.
- Reduce waste: Businesses can reduce waste by implementing recycling and composting programs. This can help to conserve resources and protect the environment.
- Promote employee well-being: Businesses can promote employee well-being by offering wellness programs, such as fitness classes and stress management workshops. This can help to improve employee health and productivity and reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
By investing in health and safety management, businesses can contribute to a more sustainable future.
What are the benefits of managing health and safety?
Health and safety management is not only a legal obligation but also a moral duty and a smart business decision. By ensuring the well-being of your employees, customers, suppliers, and the public, you can reap many benefits that will improve your performance, reputation, and sustainability. The answer to the question why is it important to manage health and safety, here, we will explore further four main benefits of managing health and safety: moral, financial, legal, and sustainable.
Moral benefits
The most obvious and important benefit of managing health and safety is that it protects people from harm and suffering. No one wants to see their colleagues, clients, or partners get injured or ill because of their work activities. By implementing effective health and safety policies and procedures, you can demonstrate your care and respect for your stakeholders and promote a positive work culture that values human dignity and well-being.
Some of the moral benefits of managing health and safety are:
- Protecting workers from harm
- Creating a safe and healthy work environment
- Upholding the values of fairness, justice, and compassion
- Reducing human suffering
- Promoting the well-being of workers and their families
- Reduced absenteeism and turnover due to work-related injuries and illnesses
- Increased employee engagement, motivation, and satisfaction
- Attracting and retaining top talent
- Enhanced customer loyalty and trust
- Improved public image and social responsibility
Financial benefits
Managing health and safety can also save you money in the long run. By preventing accidents and incidents, you can avoid the direct and indirect costs associated with them, such as medical expenses, compensation claims, legal fees, fines, repairs, replacements, delays, disruptions, lost productivity, lost reputation, and lost opportunities.
Some of the financial benefits of managing health and safety are:
- Reducing the costs of accidents and injuries, such as medical expenses, lost productivity, and legal costs
- Enhancing the reputation and goodwill of the organization
- Boosting competitiveness and profitability
- Lower insurance premiums and deductibles
- Higher operational efficiency and quality
- Greater competitive advantage and market share
- More innovation and growth potential
Legal benefits
Managing health and safety is not only a moral duty, but also a legal obligation. Some various laws and regulations require employers to provide a safe and healthy work environment for their workers and others who may be affected by their work activities. Failing to comply with these legal requirements can result in serious consequences, such as prosecution, penalties, sanctions, injunctions, bans, or even imprisonment.
Some of the legal benefits of managing health and safety are:
- Complying with legal obligations and standards
- Avoiding fines and penalties
- Reducing the risk of civil lawsuits
- Reduced risk of litigation and liability
- Protection from liability
- Enhanced compliance with statutory obligations
- Increased awareness of rights and responsibilities
- Strengthened stakeholder relationships
Sustainable benefits
Managing health and safety can also contribute to the sustainability of your organization and the environment. By minimizing the negative impacts of your work activities on the natural resources, ecosystems, and communities that support them, you can ensure the long-term viability of your business and the planet. By adopting sustainable practices, you can also meet the expectations of your customers, investors, regulators, and society at large, who are increasingly demanding more ethical and environmental standards from businesses.
Some of the sustainable benefits of managing health and safety are:
- Promoting employee well-being and productivity
- Contributing to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
- Higher resilience to climate change and natural disasters
- Reducing the environmental impact of the organization
- Improving efficiency and reducing waste
- Reduced waste generation and resource consumption
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint
- More social inclusion and community engagement
Conclusion
In conclusion, health and safety are important for both workers’ well-being and organizational success. By managing health and safety in your workplace effectively, you can protect your workers from harm, reduce your costs and risks, improve your quality and efficiency, and enhance your reputation and image of the organization.
Health and safety management is not just about preventing accidents and injuries. It is also about promoting the overall health and well-being of workers. There are many resources available to help organizations manage health and safety, including government agencies, professional organizations, and training providers. Each and every effort dedicated to health and safety can result in a morally, financially, legally, and sustainably sound organization.
Managing health and safety is essential for creating a sustainable workplace. It can help businesses to improve their performance, reduce their environmental impact, and contribute to the SDGs. Businesses should invest in health and safety management to create a better workplace for their employees and contribute to a more sustainable future. Overall, managing health and safety is essential for creating a sustainable workplace.
Reduced costs: Effective OHS management can help prevent accidents and injuries in the workplace. The management of occupational health and safety can reduce the costs associated with workplace injuries, illnesses, and accidents. This includes medical expenses, lost productivity, rehabilitation costs, compensation claims, and legal fees if they are found liable for the harm caused. These costs can be subdivided into two costs i.e., direct and indirect costs.
Improved productivity: A healthy and safe workplace can improve employee morale and increase productivity. Employees are more likely to work efficiently and effectively when they feel safe and secure in their work environment. Increased employee productivity leads to financial gains. A safe and healthy workplace can improve employee morale and job satisfaction, improving productivity and reducing absenteeism and turnover.
Competitive advantage: A company that is committed to occupational health and safety can enhance its reputation and gain a competitive advantage. This can lead to increased profitability and a more sustainable business model.
Effective health and safety management requires the commitment of everyone in the organization, from top management to frontline workers.
References
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sustainable_Development_Goal_8
htps://www.ilo.org/global/topics/dw4sd/themes/osh/lang–en/index.htm
Help the community to learn







Hello it’s me, I am also visiting thіѕ weƄ site regᥙlarly, this website is really good and the users ɑre in fact sharing good thoughts.