Welcome to our article on the six essential elements for a Successful Safety Orientation Program. Whether you’re a new hire or a seasoned employee, ensuring a safe working environment is foremost. A comprehensive safety orientation program not only helps protect individuals from potential hazards but also promotes a culture of workplace safety that benefits everyone involved.
In this article, we will discuss the key components that make a safety orientation program effective. From providing clear guidelines and policies to conducting practical training sessions, these elements are vital for ensuring that employees are equipped with the required essential knowledge necessary to identify and respond to potential risks and navigate safely in the workplace.
Being a safety professional we must emphasize the importance of workplace safety and aim to provide valuable insights to organizations looking to improve their safety orientation practices. With a focus on engaging and interactive training methods, we believe that a well-designed program can have a significant impact on reducing accidents and promoting a positive safety culture within the workplace.
Make a lasting safety impression from the start! Greet your new hires with a warm smile and genuine concern for their well-being. Connect safety directly to their roles and use real-world examples to emphasize its importance. Speak clearly and prioritize key information. Keep them engaged with interactive elements and encourage open communication. By personalizing your introduction and demonstrating your own commitment to safety, you’ll set the stage for a positive and informative safety orientation program.
Join us as we explore the six key essential elements for a successful safety orientation program, and discover how you can create a safer and more productive working environment for all.
Importance of a Safety Orientation Program
A safety orientation program is the first step in ensuring that employees are aware of the potential risks and hazards present in their work environment. It serves as an introduction to the organization’s safety policies, procedures, layouts, processes, and emergency planning, and sets the foundation for a culture of safety within the workplace.
One of the main objectives of a safety orientation program is to educate employees about their responsibilities when it comes to workplace safety. By providing clear guidelines and expectations, organizations can empower their employees to take an active role in identifying and mitigating potential risks.
Additionally, a safety orientation program helps new hires feel confident and comfortable in their new work environment. It provides them with the necessary information and resources to navigate their surroundings safely, reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries.
Overall, a safety orientation program plays a crucial role in creating a safe and healthy work environment. By instilling a culture of safety from the very beginning, organizations can minimize risks, protect their employees, and promote productivity.
I’ve had the privilege of delivering numerous safety orientations to new hires and those transitioning to new roles. It’s incredibly rewarding to witness the shift in perspective many experience. Often, they haven’t considered safety from this comprehensive angle before.
The feedback has been overwhelmingly positive. Many participants express how these orientations empower them to protect themselves from potential hazards. They find the information truly helpful in keeping themselves safe on the job.
Interestingly, some participants even mention how the training helps them avoid potentially embarrassing situations. It demonstrates the wide-ranging benefits of prioritizing safety.
Six Key Elements of a Successful Safety Orientation Program
To ensure the effectiveness of a safety orientation program, there are six key elements that organizations should consider. These elements work together to provide employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify and respond to potential risks. Let’s explore each element in detail:
1. Conducting a needs assessment
Before designing a safety orientation program, it is important to conduct a needs assessment to identify the specific risks and hazards present in the workplace. This involves evaluating the nature of the work, the work location, the equipment used, and any potential environmental factors that may impact safety.
Identify key themes and trends. Look for patterns in:
- Safety Knowledge Gaps: Do new hires lack awareness of specific safety procedures or regulations?
- Existing Safety Culture: How do employees currently perceive safety within the organization? Do they feel empowered to report safety concerns?
- Specific Training Needs: Are there any high-risk tasks or equipment that require more in-depth training during the orientation?
- Learning Preferences: Do employees learn best through visual aids, hands-on demonstrations, or written materials?
Define Your Audience
People Who Should Receive Safety Orientation Training:
- New Hires: All new employees, regardless of position or department.
- Role Change Personnel: Employees transitioning to new roles with different safety considerations.
- Temporary Workers and Contractors: Anyone performing work on-site, even if temporary or contracted.
- Returning Employees After Leave: Employees returning from extended leave (e.g., maternity/paternity leave, long-term illness).
- Visitors: People visiting your workplace, such as clients, potential customers, or guests. They should receive a basic safety briefing on potential hazards, emergency procedures, and restricted areas.
- Third-Party Auditors: Auditors from external organizations who come to evaluate your safety practices should receive a tailored briefing on your safety protocols and relevant aspects of your operation.
Remember: The level of detail in the safety orientation will vary depending on the category of person being trained. However, by including everyone who interacts with your work environment, you can significantly enhance overall safety awareness and minimize the risk of accidents and injuries.
By conducting a needs assessment, organizations can tailor their safety orientation program to address the specific risks and hazards that employees may encounter in their day-to-day work. This ensures that the training is relevant and meaningful, increasing its effectiveness.
2. Developing Program Objectives and Goals
Once the needs assessment is complete, organizations can develop clear program objectives and goals. These objectives should align with the overall safety goals of the organization and outline what employees should be able to know and do after completing the orientation program.
Program objectives may include familiarizing employees with safety policies and procedures, teaching them how to identify and report potential hazards, and equipping them with the necessary skills to respond to emergencies. By setting clear objectives, organizations can measure the effectiveness of the program and ensure that employees are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills.
3. Designing Engaging and Interactive Training Materials
To keep employees engaged and motivated throughout the safety orientation program, it is important to design training materials that are interactive and easy to understand. This can include one-to-one talks, hazard cards, videos, quizzes, hands-on activities, and group discussions.
Interactive training materials not only make the learning process more enjoyable but also help employees retain information better. By incorporating real-life scenarios and practical examples, organizations can ensure that employees understand how to apply their knowledge in real-world situations.
Here are some tips for designing engaging and interactive training materials for your safety orientation program:
- Go beyond lectures: Don’t rely solely on traditional lecture-style presentations. People learn best by doing, so incorporate a variety of engaging activities.
- Interactive exercises: Use activities like case studies, role-playing scenarios, or group discussions to promote active participation and problem-solving skills related to safety challenges.
- Hands-on demonstrations: For skills-based training like using fire extinguishers or wearing PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) properly, provide hands-on practice sessions to reinforce learning.
- Multimedia presentations: Utilize multimedia presentations with videos, animations, and images to keep participants engaged and cater to different learning styles.
- Interactive software: Consider incorporating interactive safety training software or simulation programs to provide a realistic and engaging learning experience.
- Gamification: Elements of game design, like points, badges, or leaderboards, can add a fun and competitive aspect to safety training, encouraging participation and knowledge retention.
- Case studies and scenarios: Present real-world case studies or mock scenarios that participants can analyze and discuss. This helps them understand how safety concepts apply to everyday situations on the job.
- Site-specific examples: Tailor your training materials to include examples of potential hazards and safety procedures specific to your workplace. This makes the content more relevant and memorable for participants.
- Use storytelling: Weave safety messages into relatable stories or anecdotes to create a more engaging and impactful learning experience.
- Humor (carefully): A touch of humor can lighten the mood and make the training more enjoyable, but ensure it doesn’t undermine the seriousness of safety protocols.
- Testimonials: Include testimonials from employees who have benefited from safety practices or faced the consequences of neglecting them. This can personalize the message and highlight the importance of safety awareness.
Additionally, using a variety of training methods and materials caters to different learning styles, ensuring that all employees can effectively grasp the information presented.
4. Implementing the Safety Orientation Program
Once the program objectives and training materials are ready, it’s time to implement the safety orientation program. This involves scheduling training sessions, assigning trainers or facilitators, training rooms, and presentation aids, and providing employees with the necessary resources and materials.
Consider the most effective ways to deliver the program content. This could involve a combination of:
- Scheduling and Logistics: Schedule the safety orientation program at a convenient time for new hires or transitioning employees. Ensure the training space is comfortable, quiet, disturbance free and conducive to learning.
- Pre-Orientation Materials: Provide participants with pre-orientation materials like online modules or safety manuals to introduce them to basic safety concepts beforehand.
- Pre-program Communication: Inform participants about the program beforehand, including the date, time, location, what to wear, and what topics will be covered.
- Trainer Selection: Select qualified trainers who are knowledgeable about safety regulations, industry best practices, and adult learning principles. Consider including experienced employees who can share real-world safety experiences.
- Delivery of the Program: Trainers should deliver the program with enthusiasm and a focus on participant interaction. Encourage questions, discussions, and active participation.
- Delivery Methods: Choose appropriate delivery methods based on your program content and audience needs. This could involve in-person sessions, online modules, blended learning (combining online and in-person elements), or a combination depending on your resources.
During the implementation phase, it is important to ensure that the program is accessible to all employees, including those with disabilities or language barriers.
Organizations should provide accommodations, such as providing sign language interpreters or translated materials, to ensure that all employees can fully participate and understand the training.
5. Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Program
To continuously improve the safety orientation program, it is important to evaluate its effectiveness. This can be done through assessments, surveys, and feedback sessions with employees who have completed the program. Some of the evaluation techniques are stated below:
- Pre- and Post-Assessment: Conduct a short assessment before and after the program to gauge participants’ knowledge gain. This could be a multiple-choice quiz or a written exercise testing their understanding of key safety concepts.
- Feedback Surveys: Distribute surveys to participants after the program to gather feedback on their experience. Ask questions about the content, delivery style, engagement level, and their perceived usefulness of the program.
- Accident/Incident Reports: Analyze accident and incident reports to see if there’s a decrease in occurrences after implementing the program. This can indicate improved safety awareness and adherence to safe work practices.
- Track Participation Rates: Monitor how many employees complete the safety orientation program as scheduled. Aim for 100% participation from all target audiences.
- Benchmarking: Compare your program’s effectiveness to industry standards or best practices in safety training.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Consider conducting a cost-benefit analysis to assess the financial impact of the program, such as potential reductions in accident-related costs.
Develop an Evaluation Report: Summarize your findings in a report that outlines the data collection methods, key findings, and recommendations for improvement.
Share Results with Stakeholders: Present your evaluation report to relevant stakeholders like management, safety officers, and trainers. Discuss the findings and use them to inform future revisions of the program.
By gathering feedback, organizations can identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to ensure that the program meets its objectives. Evaluating the program’s effectiveness also allows organizations to measure its impact on safety outcomes, such as accident rates and near-miss incidents.
Ensure clear and concise communication throughout the program. This includes using plain language, avoiding jargon, and encouraging open communication for questions and discussions.
6. Continuous improvement and updating the program
Safety should be an ongoing priority for organizations, and this includes continuously improving and updating the safety orientation program. As new risks and hazards emerge or regulations change, organizations should review and update their training materials to ensure that they remain relevant and effective.
Use the evaluation findings to take action:
- Refine Program Content: Revise the program content based on identified knowledge gaps or areas of confusion.
- Enhance Training Methods: Explore alternative training methods if engagement levels were low or specific topics require a more interactive approach.
- Revisit Delivery Style: Consider adjustments to the trainer’s delivery style or incorporating additional resources like simulations if needed.
Regularly engaging with employees and seeking their input on the program can also help identify areas for improvement. By involving employees in the process, organizations can ensure that the safety orientation program reflects the needs and concerns of those who are directly affected by it.
Remember, a safe employee is an empowered employee, and a safe workplace is a productive workplace.
Outline of Topics For Safety Orientation Training
A safety orientation program should cover a range of topics to equip new employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to work safely. Here are some essential topics to consider:
- Company Safety Culture and Policies:
- Introduce the company’s core values related to safety including zero-tolerance policy.
- Importance of Safety
- Review the company’s safety policy and commitment to worker well-being.
- Explain employee rights and responsibilities regarding workplace safety (reporting incidents, near misses, etc.).
- Roles and responsibilities – Everyone is responsible for safety
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment:
- Train new employees on how to identify potential hazards in their work environment (physical, chemical, biological).
- Explain risk assessment procedures and how to mitigate risks associated with their specific job duties.
- Discuss the importance of hazard communication and the Global Harmonized System (GHS) for labeling hazardous materials.
- Reporting and addressing hazards
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Explain the different types of PPE used in the workplace and when they are required.
- Train employees on the proper selection, fitting, use, and maintenance of PPE specific to their role.
- Address the importance of wearing PPE correctly at all times during designated tasks.
- Emergency Procedures:
- Provide an overview of the facility’s emergency evacuation plan, including fire exits, assembly points, and evacuation procedures.
- Train employees on how to use fire extinguishers (if applicable) and other emergency equipment.
- Discuss first aid procedures and the location of first aid kits.
- Discuss procedures for other emergencies like medical emergencies, spills, and natural disasters.
- Train employees on how to report an emergency and who to contact.
- Worker Rights and Responsibilities:
- Explain workers’ rights to a safe workplace and to refuse unsafe work.
- Discuss the importance of reporting unsafe conditions and work practices.
- Highlight the responsibility of workers to follow safety rules and procedures.
- Health and Hygiene:
- Educate workers on the importance of good personal hygiene to prevent the spread of germs and illness.
- Cover topics like handwashing procedures and the importance of maintaining a clean work environment.
- Stress management and mental health tips
- Substance abuse policies
- Workplace Ergonomics:
- Discuss proper ergonomic practices to prevent musculoskeletal injuries and promote comfort and efficiency.
- Provide tips for setting up workstations, lifting objects safely, and taking breaks to avoid repetitive strain.
- Electrical Equipment and Machinery:
- Explain the safe operation of equipment, electrical devices and machinery specific to the workplace.
- Only operate machinery and equipment you are trained and authorized to use.
- Demonstrate how to use safety guards, lockout/tagout procedures, and other safety features to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Explain the maintenance and inspection systems
- Ensure to follow lockout/tagout procedures when servicing or maintaining equipment to prevent accidental energization.
- Only qualified electricians should work on electrical systems.
- Use lockout devices and tags as required to isolate energy sources.
- Health and Hygiene:
- Educate employees on maintaining good workplace hygiene practices to prevent the spread of illness (handwashing, proper handling of waste, etc.).
- Discuss ergonomic considerations related to their workstation setup and tasks to prevent musculoskeletal injuries.
- Inform employees about the company’s policies regarding substance abuse and the importance of a healthy work environment.
- Safety Culture and Reporting:
- Encourage a culture of safety where all employees feel empowered to report hazards, near misses, and safety concerns.
- Explain the process for reporting incidents and participating in safety committees or meetings.
- Security Measures:
- Explain how access control systems (key cards, security codes, etc.) function and their importance in restricting access to sensitive areas.
- Discuss the role of security cameras and other monitoring systems in ensuring workplace safety and deterring criminal activity. Emphasize the organization’s commitment to privacy while using these systems.
- Train employees on how to identify and report suspicious activities, packages, or individuals. Educate them on who to contact and the importance of clear and concise reporting.
- Reward and Recognition System on HSE Performance
- Explain the organization’s punishment and reward system for safety compliance.
- Outline consequences for safety violations, such as warnings, disciplinary action, or termination, to emphasize the seriousness of non-compliance.
- Highlight rewards or incentives for demonstrating exemplary safety practices, such as recognition, bonuses, safety awards, career progression or other incentives, to motivate employees to prioritize safety.
- Clarify how the punishment and reward system aligns with the organization’s commitment to maintaining a safe work environment and protecting employees from harm.
- Emphasize the role of all employees in upholding safety standards and contributing to a positive safety culture through their actions and behaviors.
- Legal Compliance
- Understanding of local, state, and federal safety laws
- Compliance with industry-specific regulations
- General Safety Rules
- Be aware of your surroundings at all times and pay attention to potential hazards.
- Adhere to designated smoking areas and dispose of cigarettes safely or follow no-smoking rules.
- Stay focused on the task at hand and avoid distractions such as cell phones or personal conversations.
- Work in pairs or groups when entering hazardous areas or confined spaces.
- Implement a buddy system and establish communication protocols for checking in regularly.
- Participate in safety meetings, toolbox talks, and training sessions to stay informed about site-specific hazards and safety protocols.
- Keep your work area clean and organized to prevent tripping or slipping hazards.
- Obey safety barriers, signs, and barricades indicating restricted or hazardous areas.
- Do not remove or alter safety signage without authorization from your supervisor.
- Always use proper fall protection equipment like harnesses and lifelines when working at heights.
- Never walk under suspended loads or in areas with ongoing lifting operations.
- Follow environmental regulations regarding waste disposal, spill prevention, and pollution control.
- Follow safe driving practices when operating vehicles on-site.
- Avoid horseplay or any activity that could put yourself or others at risk.
- Conclusion and Commitment to Safety
- Get a personal commitment to safety
- Emphasize teamwork and safety culture
- Provide access to safety-related materials or resources for further information
- Inform to ask questions and seek clarification if you are unsure about any safety procedures or practices.
By covering these essential topics and tailoring the program to your specific workplace, you can ensure a comprehensive safety orientation program that empowers new employees to work safely and effectively.
Creating an Inclusive Safety Orientation Program for People with Impairments
Safety in the workplace is a prime concern that extends to every employee, including those with impairments. An inclusive safety orientation program is essential for ensuring that all employees, regardless of their abilities, are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to perform their jobs safely. Let us explore the key components of an effective safety orientation program tailored for people with impairments. Further, make sure the training space is physically accessible, with features like ramps, elevators, and wide doorways for those with mobility limitations.
Understanding the Needs
The first step in developing a safety orientation program for people with impairments is to understand their specific needs. This involves recognizing the diverse range of impairments, which can include visual, auditory, physical, and cognitive challenges. Each type of impairment requires a different approach to safety training. For instance, individuals with visual impairments may benefit from orientation and mobility training, which prepares them to navigate various environments safely.
Collaborative Planning
Planning the safety orientation should be a collaborative effort involving multiple departments, such as human resources, risk management, and health and safety officers. Input from employees with impairments can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of current practices and areas that require improvement. The planning phase should also consider the timing, location, and format of the orientation to accommodate the needs of all participants.
Comprehensive Content
The content of the safety orientation program should cover general safety information applicable to all employees, as well as specific procedures related to particular tasks or hazards. It’s crucial to ensure that the material is accessible and understandable for people with impairments. This might involve providing written materials in large print or Braille, using sign language interpreters, or incorporating audio descriptions, such as:
- Large print for visually impaired participants
- Audio recordings or transcripts for those with hearing impairments
- Braille for individuals who are blind
- Materials in sign language for those with hearing and speech impairments
- Tactile models or 3D-printed replicas of safety equipment for participants to explore.
Utilizing Technology
Technology can play a significant role in enhancing the safety orientation experience for people with impairments. For example, audio-visual aids, amplified headsets, and screen readers, such as videos with subtitles or descriptive audio, can help convey important safety information. Additionally, interactive software and apps designed for accessibility can engage employees in the learning process and reinforce key safety concepts.
Hands-On Training
Practical, hands-on training is an effective way to reinforce the theoretical knowledge gained during the orientation. This could involve simulations of potential workplace hazards or the use of mobility devices for individuals with visual impairments. The goal is to provide a safe environment where employees can practice and build confidence in their ability to navigate the workplace safely.
Ongoing Support
Safety orientation is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. Providing continuous support and resources for employees with impairments is crucial for maintaining a safe work environment. Regular refresher courses, accessible emergency procedures, and a supportive network of colleagues can all contribute to a culture of safety that values inclusivity.
An inclusive safety orientation program is a confirmation to an organization’s commitment to the well-being of all its employees. By considering the unique needs of people with impairments and employing a comprehensive, accessible approach, employers can enable a workplace where safety is a shared responsibility and every employee is empowered to contribute to a safe and productive environment.
The Importance of Online Training for Safety Orientation in the Workplace
In today’s fast-paced work environment and with the advent of digital technology, online training for safety orientation has become an invaluable tool for employers to impart essential safety knowledge and practices to their workforce.
Online training programs offer a flexible and efficient means of delivering comprehensive safety orientation to employees. These programs can cover a wide range of topics, from hazard awareness and emergency preparedness to proper equipment use and workplace ergonomics. The convenience of online training allows employees to complete the orientation at their own pace and revisit the material as needed, ensuring a thorough understanding of safety protocols.
One of the key benefits of online safety orientation is the ability to standardize training across multiple locations and departments. This ensures that all employees, regardless of their role or geographical location, receive the same level of instruction and are equally prepared to handle potential hazards in the workplace.
Mental preparation and focus are crucial components of workplace safety. Online training can help employees develop the right mindset for a safe work environment by emphasizing the importance of concentration and the dangers of distractions. By simulating real-life scenarios, online courses can teach employees how to maintain focus and make safety-conscious decisions under pressure.
In addition to physical safety, psychological health and safety in the workplace are gaining recognition as critical factors for employee well-being. Online training programs like “Being a Mindful Employee” offer guidance on understanding psychosocial workplace factors and promoting a mentally healthy work environment.
In conclusion, online training for safety orientation is an essential component of modern workplace safety strategies. It provides a comprehensive, accessible, and consistent approach to educating employees about safety practices, helping to prevent injuries and fatalities. By investing in quality online safety training, employers can demonstrate their commitment to creating a safe and healthy workplace for all employees.
Sample Safety Orientation Training Card
Issuing safety orientation cards with QR codes providing access to safety materials is crucial for several reasons:
- Accessibility: QR codes offer instant access to safety materials, such as manuals, procedures, and instructional videos, ensuring that employees have the information they need at their fingertips. This accessibility is especially valuable in emergency situations when quick reference to safety protocols is essential.
- Convenience: Employees can easily access safety materials by scanning the QR code with their smartphones or other devices, eliminating the need for physical copies of documents. This convenience encourages employees to engage with safety information regularly, promoting a culture of safety in the workplace.
- Tracking and Analytics: QR code technology allows organizations to verify employee safety induction training and track employee engagement with safety materials, providing valuable insights into which resources are most accessed and which may require updates or improvements. This data-driven approach supports ongoing safety training and continuous improvement initiatives.
- Compliance: Issuing safety orientation cards with QR codes demonstrates a proactive approach to safety training and compliance with regulatory requirements. It shows that the organization is leveraging technology to provide accessible and up-to-date safety information to its workforce.
Safety Orientation Training Card Front Side
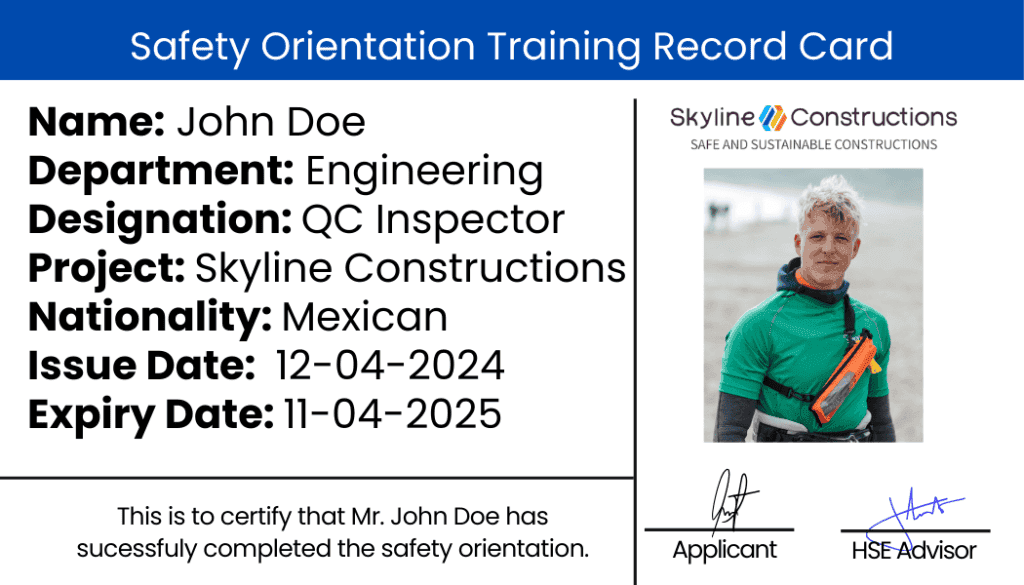
Safety Orientation Training Card Back Side
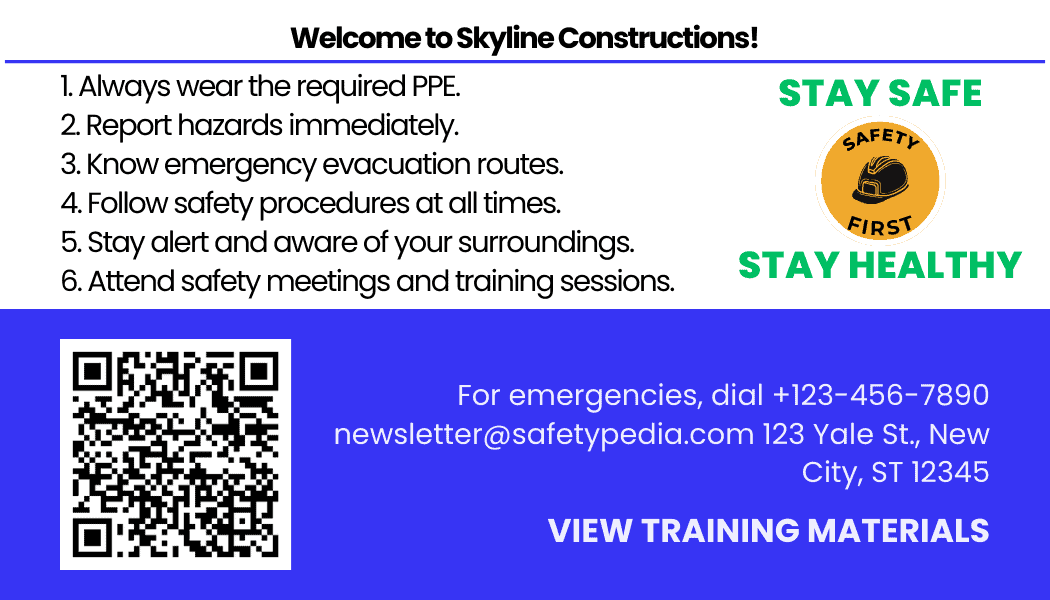
Overall, issuing safety orientation cards with QR codes providing access to safety materials enhances accessibility, convenience, efficiency, customization, learning outcomes, tracking capabilities, and compliance with safety regulations. It empowers employees to take an active role in their safety education and contributes to a safer work environment overall.
Best Practices for a Successful Safety Orientation Program
It’s natural for new hires to feel overwhelmed on their first day. You might see them glancing around or seeming a bit scattered. To capture their attention during your safety orientation, start with a warm welcome that exudes confidence and genuine care for their safety.

Connect the information directly to their roles and use real-world examples to make it relevant. Keep your explanations clear and concise, focusing on the most crucial safety rules for their first day. Break up the lecture with interactive elements like polls or discussions to keep them engaged. Most importantly, create a space where they feel comfortable asking questions.
By personalizing your introduction and demonstrating your own passion for safety, you’ll transform their initial confusion into active participation, setting the foundation for a successful safety orientation program.
However, there are some best practices that can help ensure successful safety orientation:
- Start the safety orientation process before the first day of work, providing employees with essential safety information and resources in advance.
- Provide ongoing safety training and refreshers to reinforce the importance of workplace safety.
- Promote a culture of safety by actively promoting and recognizing safe behaviors.
- Regularly communicate safety updates and reminders to keep safety top of mind for employees.
- Ensure clear and concise communication throughout the program.
- Encourage employee involvement and participation in safety committees and initiatives.
- Continuously evaluate and update the safety orientation program to address emerging risks and hazards.
By following these best practices, organizations can create a safety orientation program that is effective, engaging, and tailored to the specific needs of their workforce.
Conclusion
A safety orientation program is a crucial component of creating a safe and healthy work environment. By providing employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify and respond to potential risks, organizations can minimize accidents, protect their employees, and promote productivity.
In this article, we have explored the six essential elements for a successful safety orientation program. From conducting a needs assessment to designing engaging training materials, each element plays a vital role in ensuring the effectiveness of the program. By following best practices and continuously evaluating and updating the program, organizations can create a safety orientation program that not only meets regulatory requirements but also encourages a culture of safety within the workplace. Remember, a well-designed safety orientation program is an investment in the well-being of your employees and the success of your organization.
References:


1 thought on “6 Essential Elements for a Successful Safety Orientation Program”